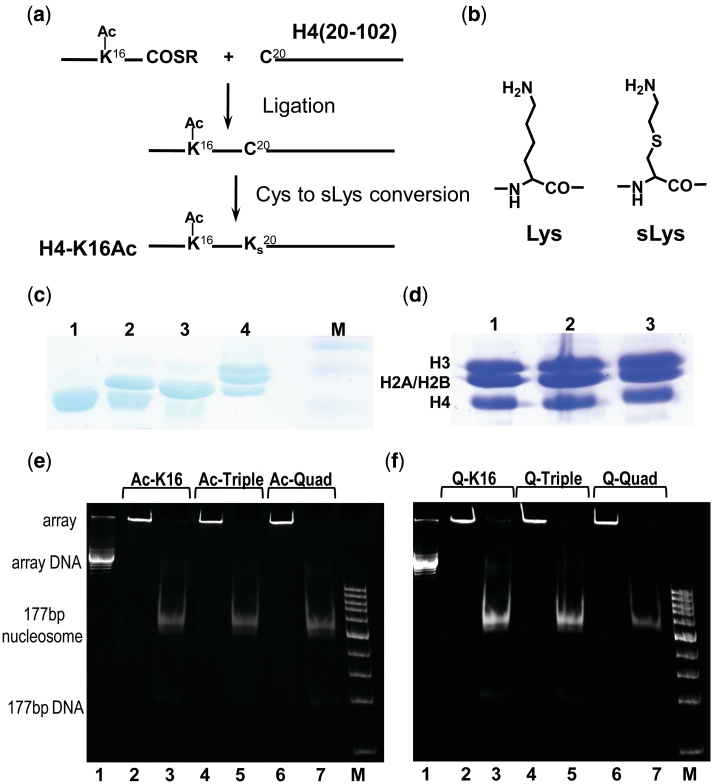
Figure 1.
(a and b) Scheme for the semi-synthesis preparation of histones with covalently modified histone N-terminal tails by Native Chemical Ligation (NCL) in combination with S-alkylation. Amino acids 1–19 of the histone H4 with lysines acetylated at selected positions were manually synthesized by the Boc-based SPPS method and ligated to the recombinantly prepared variant of the H4 histone [amino acids 20–102 with K20C mutation, H4(20-102)K20C]. (a) Preparation of H4K16-Ac. First step: Ligation to form an Arg19-Cys20 junction. Second step: Conversion of Cys20 to sLys20 by treatment with bromoethylamine. (b) Comparison of Lys and sLys. (c) 18% SDS–PAGE illustrating production of the HO with H4-K16Ac histone: lane 1—globular H4(20-102)K20C (before ligation); lane 2—mixture of H4(20-102)K20C and ligation product (H4(K16Ac,K20C); lane 3—purified H4 K16Ac; 4—HO with H4 K16Ac; M—marker. (d) 18% SDS–PAGE of the HOs with acetylated forms of the histone H4. Lane 1, HO with tetra-acetylated H4 K5,8,12,16Ac; lane 2, HO with tri-acetylated H4 K5,8,12 Ac; lane 3, HO with H4 K16Ac. (e and f) Characterization of purity and saturation of the 12-177-601 nucleosome arrays containing (e) acetylated and (f) K→Q mutated histone H4. Array identity is indicated on the top of the lanes. In (e and f), lanes 2,4,6 are for the ScaI untreated array; lanes 3, 5 and 7 for the array after ScaI digestion; lanes 1 is 12-177-601 DNA; M is DNA marker from 100 to 1500 bp, step 100 bp.