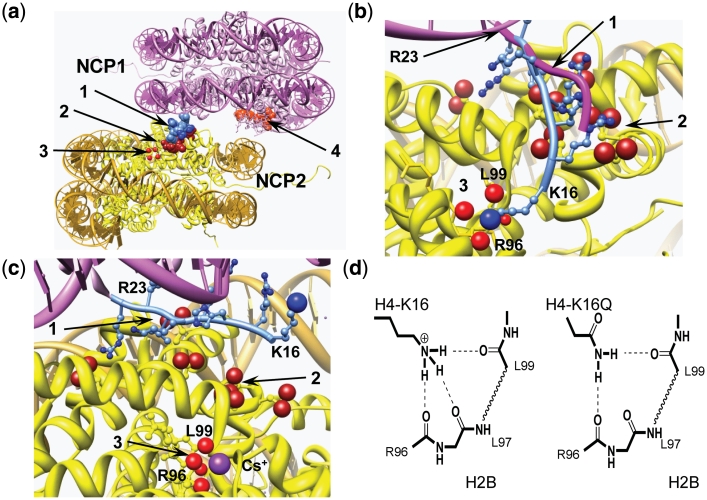
Figure 7.
Structural analysis of NCP–NCP stacking. (a) NCP–NCP contact in the crystal 1AOI (1) with important domains involved in formation of the contact shown in space filling: 1 light blue, H4 K16-R23 of the NCP1; 2 dark red, acidic islet of the H2A histone (amino acids E56, E61, E64, D90, E91, E92) in the NCP2 interacting with H4 K16-R23 domain of the NCP1; 3 four red spheres, carbonyl atoms of the main chain peptide H2B R96-L99 of the NCP2; 4 light red, acidic islet of the H2A histone of the NCP1 needed to be screened in stacking contact. (b) Detailed presentation of the H4 K16-R23 binding to the neighboring NCP2 with hypothetical relocation of the H4-K16 from the acidic H2A patch to the H2B R96-L99-binding site. To accommodate the H4-K16 ε-amino group coordination with the H2B R96-L99 carbonyl groups, the NCP1 was moved 2 Å towards the H2B site and the structure of the H4 K16-R23 fragment (shown in light blue with H4-K16 ε-amino group as a blue sphere) was engineered by manipulating torsion angles. The original location of the H4 K16-R23 chain in the 1AOI crystal is indicated by magenta tracing of the peptide backbone. (c) The same region of the NCP–NCP contact as in (b) but built using the crystal structure of the NCP saturated with Cs+ [3MGS (58)]. The Cs+ ion coordinated with R96, L97, L99 carbonyl oxygen atoms is seen at the bottom of the cartoon. In (b) and (c), domains are numbered as in (a) with charged oxygen atoms of the carboxylate group in the acidic islet of the H2A histone highlighted as red spheres. (d) Proposed hydrogen bonding of the H4-K16 binding to the crystallographically determined Rb+/Cs+-binding pocket in (c). To the left is shown the proposed native K16 ε-amine hydrogen bonding and the right demonstrates alternative hydrogen bonding upon K→Q mutation of H4-K16, which maintains this structural element. Acetylation is suggested to completely disrupt this binding due to steric constraints and reduced H-bonding capacity. Chimera visualization and molecule editing package (63) was used to build the structures in a–c.