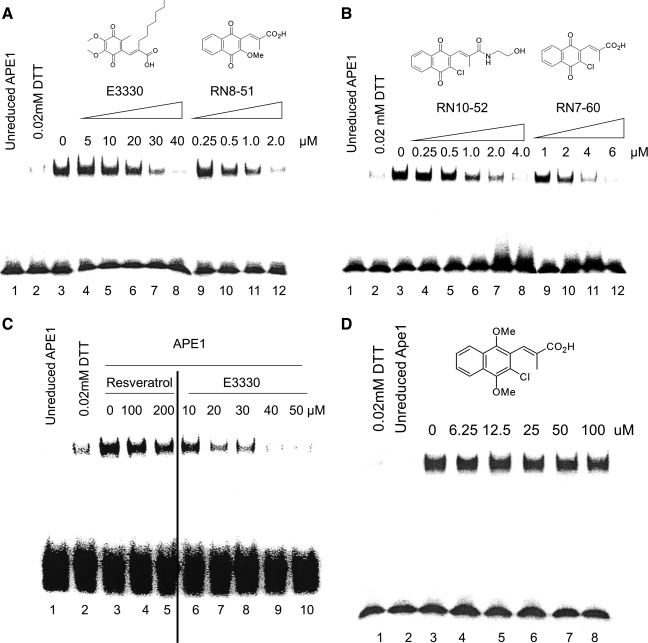
FIG. 2.
E3330 analogues blocked APE1 redox function in EMSA assay. Increasing amounts of E3330 or its analogues (RN8-51, RN10-52, and RN7-60) were incubated for 30 min with 2 μl purified hAPE1 (reduced with 1.0 mM DTT, then diluted to 2 μg/ul with 0.2 mM DTT in PBS) in EMSA reaction buffer [10 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 5% (vol/vol) glycerol] with a total volume 10 μl. EMSA was performed with reduced APE1 and 0.02 mM DTT, which was the amount of DTT carried over from the reduction of APE1 as control. (A) RN8-51; (B) RN10-52, and B) RN7-60 inhibited AP-1 DNA-binding enhanced by APE1 in a dose-dependent manner, with a much lower IC50 (0.5, 0.75, and 1.5 μM, respectively) than E3330 (20 μM). Increasing amounts of resveratrol (C) or analogue RN7-58 (D) were incubated for 30 min with 2 μl purified human APE1 (reduced with 1.0 mM DTT, and then diluted to 2 μg/ul with 0.2 mM DTT in PBS) in EMSA reaction buffer [10 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 5% (vol/vol) glycerol] with a total volume 10 μl. EMSA was performed with unreduced APE1 and 0.02 mM DTT, which was the amount of DTT carried over from the reduction of APE1 as control. Neither compound showed any inhibitory effects. Experiments were repeated 3 times with similar results, as shown.