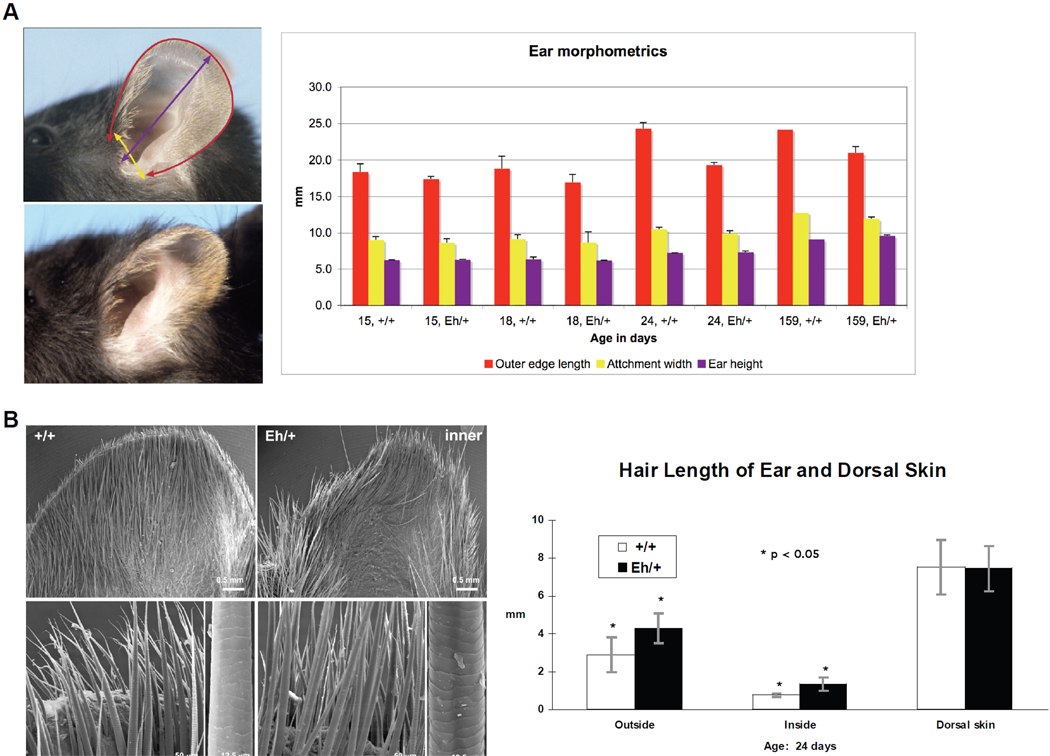
Figure 2. Hair phenotype of the hairy ears (Eh) mutation.
A: Ear morphometrics are colour-coded. The red, yellow, and purple columns in the chart represent the measurements (mean with standard deviation) of ear outer edge length, attachment width, and height, respectively, as illustrated by the mouse ear images on the left. The measurements are in millimetres (mm, y axis) for postnatal days 15, 18, 24, and 159 (x axis) mice. The specimens were from mice on the C57BL/6ByJ background. B: SEM images of the inner surface of the pinna (specimens were from mice on C3H/Rl background) and the hair length (mean with standard deviation) for pups of postnatal day 24 (specimens were from mice on C57BL/6J background). Higher magnification in the SEM images shows that the ear-specific hair fibres remain the same type on the Eh/+ as on the +/+ ears. Images of the outer side of the ears are not shown. The scale bars are indicated. Hair length in mm (y axis) is plotted for the interior and the exterior of ears and for dorsal skin and the standard deviations were given.