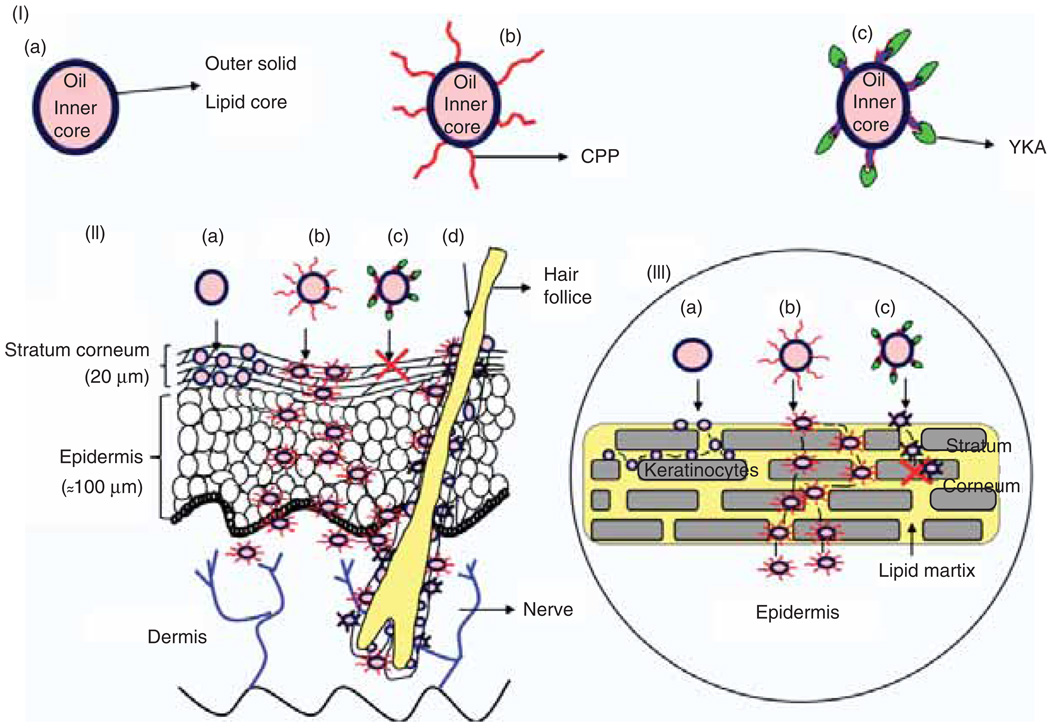
Figure 1.
Model for topical delivery of CPP-coated NLC delivery approach. (I) Structures of NLC with and without surface modifications. (a) Structure of NLC; (b) Structure of CPP-coated NLC (NLC-CPP); (c) Structure of non-transduction peptide, YKA, coated NLC (NLC-YKA). (II) Various pathways for the entry of nanoparticles into the skin. (a) This panel shows that due to occlusive properties, NLC particles entering into the stratum corneum via the paracellular route are unable to cross SC; (b) Surface modification of NLC particles with CPP favours permeation of NLC into the SC and subsequently into the epidermis; (c) YKA coating on NLC prevents entry of nanoparticles into the skin, (d) NLC and NLC-CPP enter the skin via hair follicle route. (III) An expanded view of the SC and NLC penetration mechanisms (see legend to Figure 1, part II for description).