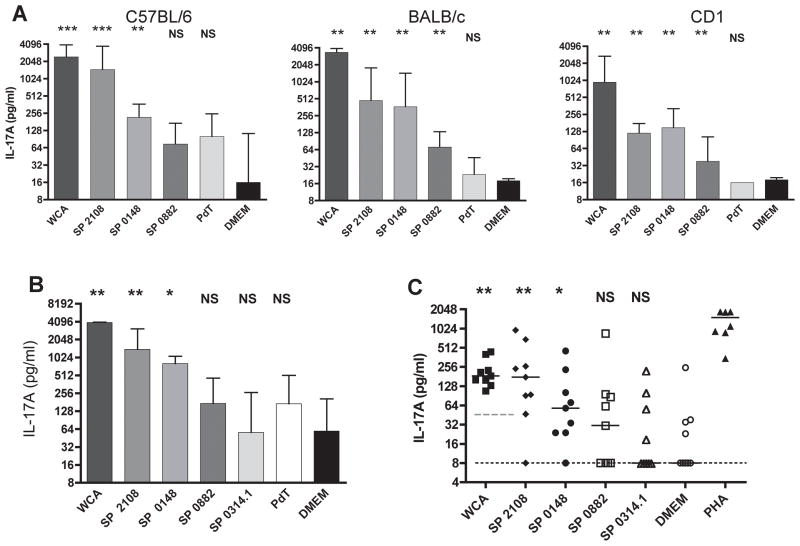
Figure 1. SP2108 and SP0148 are recognized by TH17 cells of mice colonized with pneumococcus and adult human volunteers.
(A) Antigen-specific IL-17A secretion by splenocytes isolated from mice after intranasal exposure to live pneumococcus three times at one week intervals. Bars represent median IL-17A values with interquartile range. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 by Mann-Whitney test when compared with secretion of IL-17A in response to medium (DMEM) alone. NS=not statistically different (B) Antigen-specific IL-17A secretion by splenocytes of C57BL/6J mice ten days following a single intranasal exposure to live pneumococcus. (C) The amount of IL-17A secreted by human PBMC stimulated with the indicated antigen. 9 of 11 donors had a response to WCA above the 50 pg/ml IL-17A cutoff (dashed grey line). Only WCA responders are shown here and were included in analysis. Each symbol represents the IL-17A value from a single donor with the GFP-induced IL-17A response subtracted. Median GFP value was 52 pg/mL. Bars represent median values. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 by paired Wilcoxon rank sum test when compared with IL-17A secretion following stimulation with GFP for the protein antigens or DMEM alone (median DMEM value at limit of detection; dotted black line) for WCA. NS=not statistically different.