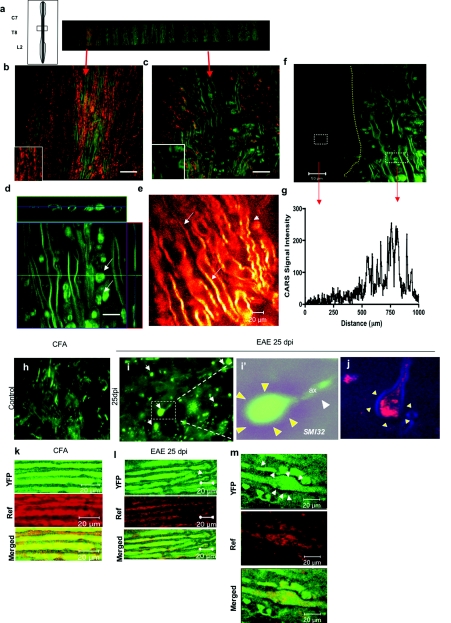
Figure 6.
Combination CARS and reflectance demonstrate axonal dysfunction and demyelination in the spinal cord. (a) Diagram and low-power map of a spinal cord slice of an EAE animal; several areas were highlighted for further analysis. (b) CARS imaging (green) combined with reflectance (red) allows one to observe the normal parallel distribution of myelinated axons in the spinal cord. (c) CARS signal during EAE at 30 dpi, with areas of complete loss of reflectance signal and areas of demyelination with dilatation of myelin sheaths. (d) Z-stack reconstruction of a dilated myelin sheath in EAE spinal cord, and accumulation of myelin debris (arrows). Bar = 20 μm. (e) Glow scale of CARS imaging in EAE spinal cord showing decrease in CARS signals in normal-appearing myelin (arrows) and tortuosity in myelin sheath (arrowhead). (f) CARS imaging showing border of demyelinating lesion in the spinal cord of EAE mice (dotted lines); the myelinated area show tortuosity of myelin sheath and myelin debris. (g) Quantification of CARS signal in demyelinating lesion, pixel intensity demonstrating total loss of CARS signal in the EAE lesion. (h) Confocal imaging of axonal SMI-32 staining in the normal spinal cord, showing typical distributions of axons, without abnormalities. (i) Confocal imaging of SMI-32 staining of EAE, showing an increase in formation of ovoids (arrows), transected axons (white arrowheads) that end in accumulation of microtubules (arrows), shown in inset i’. (j) Visualization by CARS-reflectance imaging of axonal ovoids, with dilatation of axons surrounded by myelin (blue). (k) Visualization of YFP and reflectance signals in CFA-treated animals showing strong signal and colocalization of both imaging modalities. (l) Visualization of YFP and reflectance signals in diseased animals showing decrease in the YFP signal (arrow) with similar decrease in reflectance. (m) Axonal ovoid visualized with YFP (arrows), and reflectance. Bar = 20 μm. (Color online only).