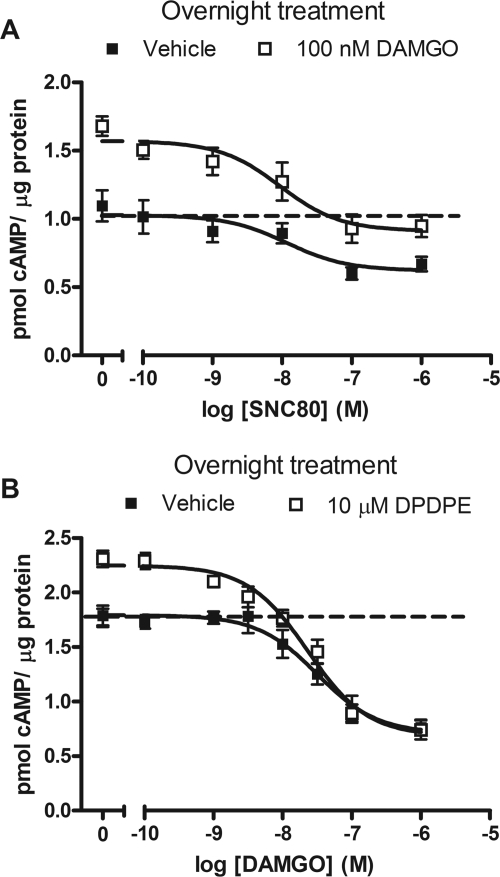
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of cAMP by MOR or DOR agonists is similar for sensitized or nonsensitized AC. A, SH-SY5Y cells were incubated with vehicle (■) or the MOR agonist DAMGO (100 nM, □) overnight to induce dependence. Withdrawal was precipitated with the MOR antagonist CTAP (1 μM) in the presence of 5 μM forskolin. Short-term cAMP production was inhibited by including various concentrations of the DOR agonist SNC80 in the precipitating media. The concentration-response of SNC80 to inhibit cAMP was similar in control and DAMGO-dependent cells (EC50: vehicle-treated = 14.6 ± 7.8 nM, DAMGO-treated, 13.8 ± 7.2 nM; p > 0.05 by two-tailed student's t test). B, cells were incubated with vehicle (■) or the DOR agonist DPDPE (10 μM, □) overnight to induce dependence. Receptor-specific withdrawal was precipitated with the DOR antagonist ICI 174,864 (1 μM) in the presence of 30 μM forskolin. Various concentrations of the MOR agonist DAMGO were included in the precipitating media. The concentration-response of DAMGO to inhibit cAMP production was similar in control and DPDPE-withdrawn cells (EC50: vehicle-treated, 32.2 ± 12.5 nM, DPDPE-treated, 29.0 ± 7.1 nM; p > 0.05 by two-tailed Student's t test). Data are presented as mean picomoles of cAMP per milligram of protein ± S.E.M. (n = 3 or 4, in duplicate). cAMP produced by forskolin alone is indicated by the dashed line.