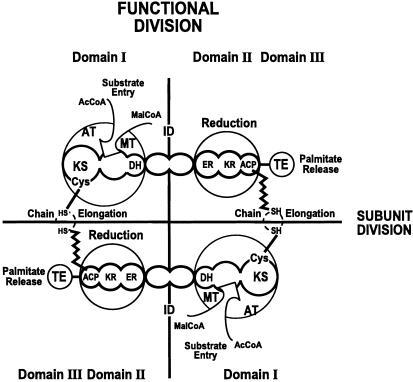
Figure 1.
The structural and functional organization of animal and human FAS dimer. The linear arrangement of the component activities and their domains are indicated in the subunits of FAS. The dimer formation results in two active centers. The functional division indicates the participation of DI of one subunit and DII and DIII of the second subunit in generating the active center. The ID regions (ID) have no known catalytic activities but play an essential role in the structural organization of catalytically active FAS. AT, acetyl transacylase; MT, malonyl transacylase; ER, enoyl reductase; KR, β-ketoacyl reductase; DH, β-hydroxyacyl dehydratase.