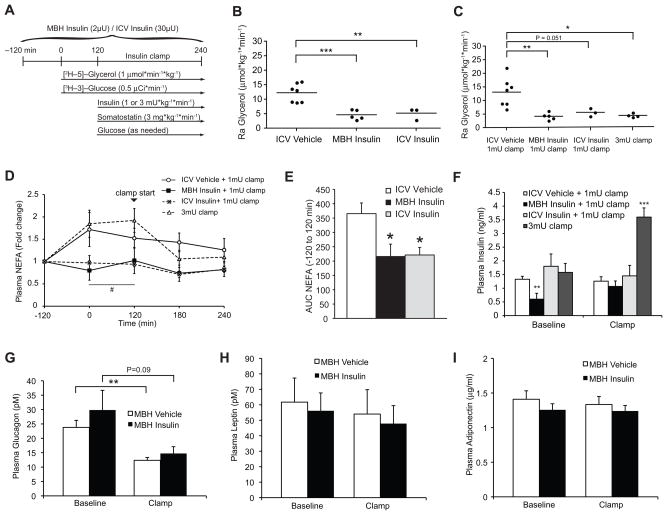
Figure 1. Brain insulin suppresses whole body lipolysis.
(A) Experimental protocol of the euglycemic clamp studies of SD rats. ICV or MBH insulin infusions were performed during basal insulin clamps (1 mU · kg−1 · min−1) and compared to rats subjected to hyperinsulinemic clamps (3 mU · kg−1 · min−1), while glycerol and glucose fluxes were determined through tracer dilution techniques. (B, C) Ra glycerol during basal (B) and clamped (C) conditions (n ≥ 3 per group). (D) Change of plasma NEFA levels compared to baseline during the 6 hr infusion protocol. Arrowhead marks the start of the clamp at time point 120 min (n ≥ 4 per group). (E) AUC of Fig. 1D comparing vehicle to ICV and MBH insulin infused rats prior to the start of the clamp study (time point -120 to 120 min, n ≥ 4 per group). (F) Plasma insulin levels during baseline (time point −120 to 120 min pre-clamp period) and the clamp (120 to 240 min, n ≥ 6 per group). (G, H, I) Plasma glucagon, leptin and adiponectin levels of MBH vehicle and insulin infused rats at baseline and the clamp (n ≥ 6). All error bars are s.e.m.; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 versus vehicle + 1 mU · kg−1 · min−1 clamp group if not otherwise indicated. # P < 0.05 versus vehicle + 3 mU· kg−1 · min−1 clamp group. (See also Fig. S1)