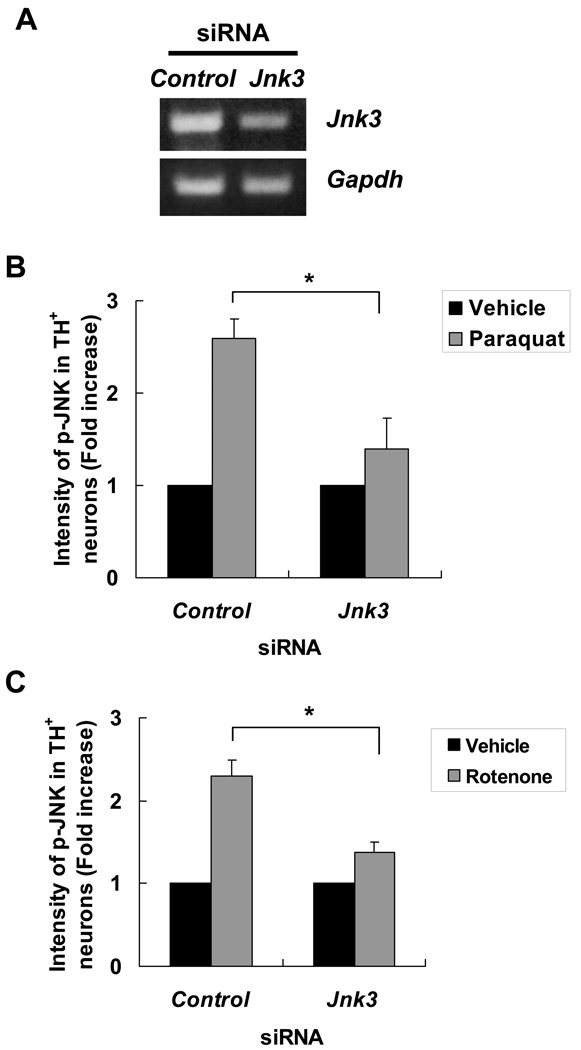
Figure 2.
JNK3 is the major JNK isoform in dopaminergic neurons activated by paraquat or rotenone. (A) Transfection of siRNA specific for Jnk3 reduces Jnk3 mRNA levels. E14 mesencephalic neurons were transfected with Jnk3 siRNA or control siRNA. Total mRNA was purified 24 hours later and analyzed by semiquantitative RT-PCR. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as an internal control. (B, C) Jnk3 siRNA reduced paraquat- (B) or rotenone (C)-induced JNK activation in dopaminergic neurons. At 24 hours after siRNA transfection, cultures were treated with 40 μM paraquat, 5 nM rotenone or their respective vehicle controls for another 8 hours. Cells were fixed and stained for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and p-JNK. The intensity of JNK phosphorylation in TH+ dopaminergic neurons was quantified. *p < 0.05.