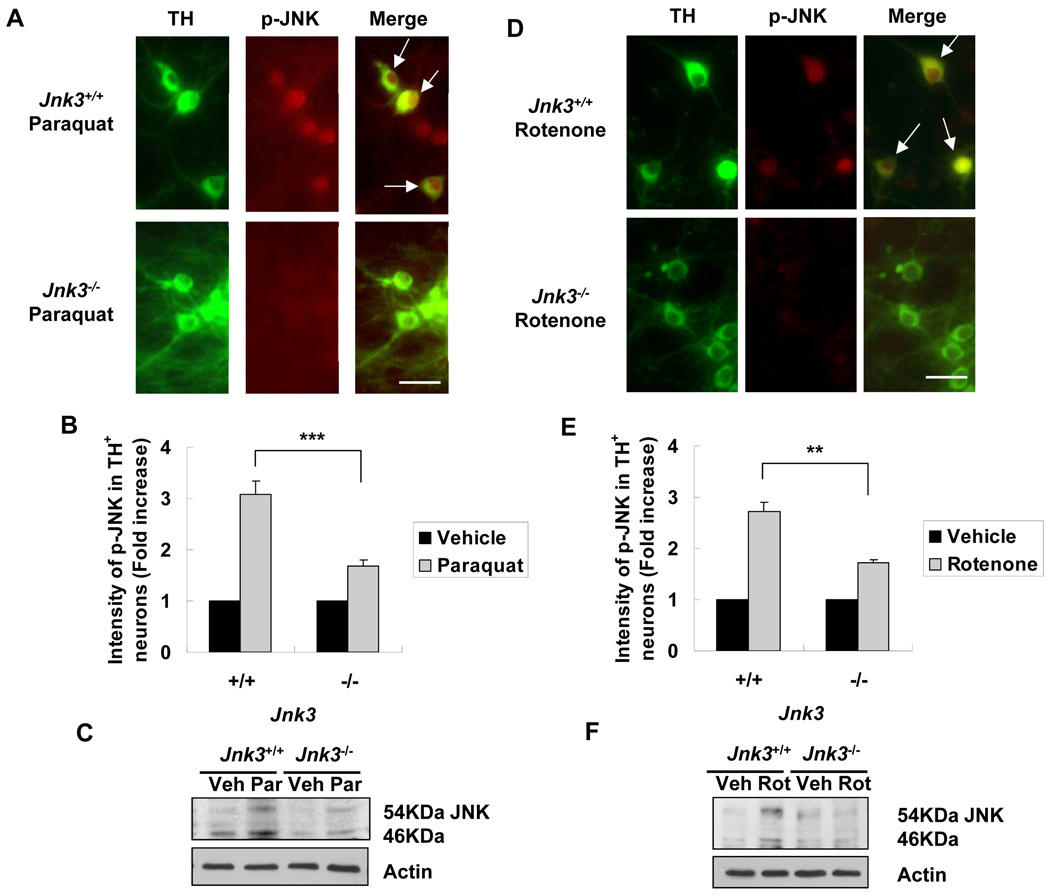
Figure 4.
Deletion of the Jnk3 gene diminishes JNK activation in culture in response to paraquat and rotenone. Jnk3 heterozygotes (Jnk3+/−) were mated and primary mesencephalic neurons were cultured separately from each E14 mouse fetus. At 6 days, cells were treated with 40 μM paraquat, 5 nM rotenone, or vehicle control for another 8 h. Cells were then fixed and immunostained for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and p-JNK. (A, D) Representative photomicrographs of cells immunostained for p-JNK and TH after treatment with paraquat (A) or rotenone (D). Arrows point to dopaminergic neurons with JNK phosphorylation. Scale bar = 20 µm. (B, E) Quantification of JNK phosphorylation in TH+ dopaminergic neurons. (C, F) After 8 hours of paraquat (C) or rotenone (F) treatment, cells were lysed and total protein was analyzed by immunoblotting for p-JNK. Actin was used as a loading control. Veh: vehicle; Par: paraquat; Rot: rotenone. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005.