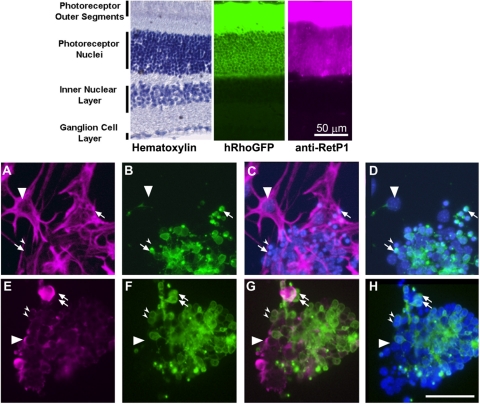
Figure 1.
Immunostaining of mixed retinal cultures from P10 tsA58/+; HRhoGFP/+ mice. Top: cryosections of the retina of an adult HRhoGFP mouse showing hematoxylin staining (left), HRhoGFP epifluorescence of the eGFP-tagged human rhodopsin transgene in the rod photoreceptors (center), and immunostaining for rhodopsin (right). Prominent fluorescence of the rhodopsin-GFP and rhodopsin immunostaining is present in the outer segments and plasma membranes of the rod photoreceptor cell bodies in the outer nuclear layer. Bottom: epifluorescence photomicrographs of mixed retinal cultures from dissociated retinas of PN10 tsA58/+; HRhoGFP/+ double heterozygous mice. (A) Vimentin immunostaining. (B) Same field as (A) but showing HRhoGFP fluorescence of rod photoreceptors. (C) Overlay of (A) and Hoechst nuclear staining. (D) Overlay of (B) and Hoechst nuclear staining. (A–D, large arrowheads) Nuclei of vimentin-positive adherent cells. Arrows: HRhoGFP-positive rod photoreceptors. Small arrowheads: vimentin-negative, HRhoGFP-negative cells. (E) Protein kinase C alpha (PKC) immunostaining. (F) Similar to (E) showing HRhoGFP fluorescent rod photoreceptors. (G) Overlay of (E) and (F). (H) Overlay of (E) and Hoechst nuclear staining. (E–G, large arrowheads) PKC-positive; HRhoGFP-negative cells. Arrows: PKC-negative; HRhoGFP-positive cells. Small arrowheads: cells positive for both PKC and HRhoGFP. Scale bars, 50 μm.