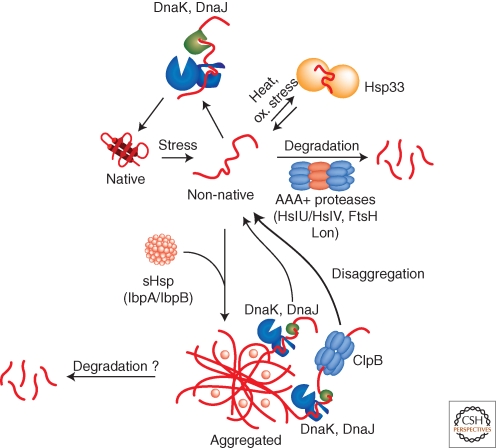
Figure 3.
Activities of bacterial quality control systems during environmental stress. Environmental stress like heat shock can cause protein-unfolding leading to the accumulation of misfolded protein species. Misfolded proteins are either refolded by the DnaK chaperone and its co-chaperone DnaJ or are removed by AAA+ proteases including e.g., Lon, ClpC/ClpP or HslU/HslV. The holding chaperone Hsp33 becomes important under oxidative and thermal stress and prevents protein aggregation. Severe stress conditions can overburden the protective capacity of quality control systems causing protein aggregation. sHsps coaggregate with misfolded protein species thereby changing the architecture (physical properties) of aggregates and allowing for more efficient protein disaggregation by chaperones. DnaK/DnaJ in cooperation with the AAA+ chaperone ClpB efficiently solubilize protein aggregates by extracting single unfolded protein species, whereas DnaK/DnaJ alone have limited disaggregation capacity. AAA+ proteases (ClpC/ClpP) might also act on aggregated protein species.