Figure 2.
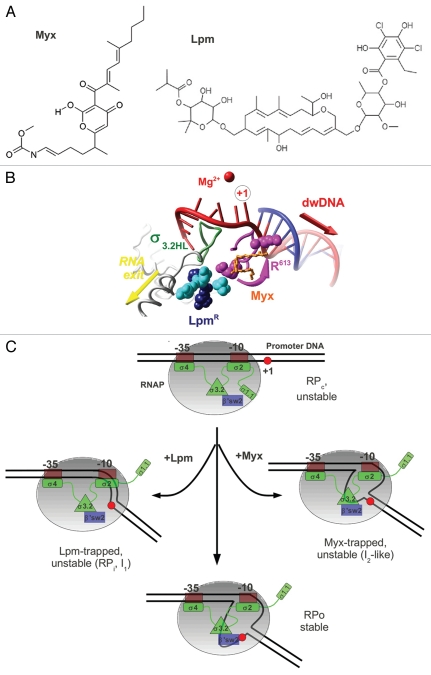
(A) Chemical structures of Myx and Lpm. (B) Overlap of the Lpm and Myx binding sites. Amino acids substitutions conferring resistance to Lpm27 are shown in CPK colored in cyan for β subunit (T. thermophilus Q1018, V1087, N1064) and magenta (R613) or dark blue (R87, P526) for β' subunit, σ3.2HL is shown as green ribbons and Myx is shown in ball-and-stick and orange. R613 is shown in two conformations—as in holoenzyme and as in the RNAP-Myx complex.1 (C) Model of the mechanism of Lpm and Myx action. RNAP core is shown as a gray ellipse. The σ subunit is shown in green, region 3.2 is shown as a green triangle, and the β' switch-2 is shown as a blue rectangle. The +1 base of the promoter is indicated by a red circle.