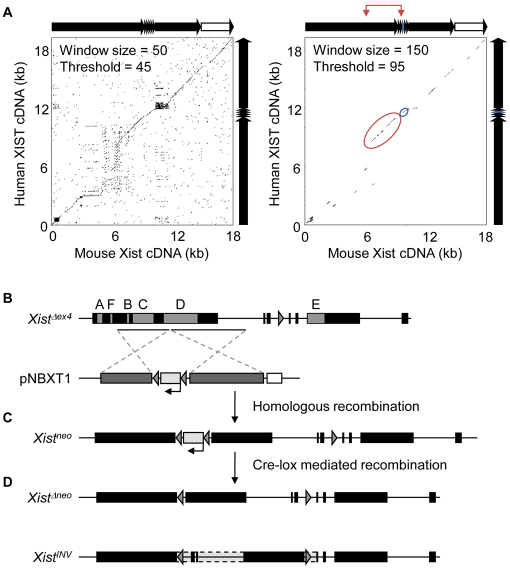
Fig. 1.
Strategy for generating a targeted inversion of Xist exon 1 conserved sequences. (A) Dotplot analysis of mouse and human Xist/XIST cDNA. Full length mouse and human Xist/XIST cDNA sequences were compared by dotplot analysis using the EMBOSS dotmatcher program (Rice et al., 2000). Two sets of parameters with different stringencies were used to demonstrate overall homology between two sequences (window size 50, threshold 45) or to highlight longer stretches with high homology (window size 150, threshold 95). Exon structure for each transcript is shown above (mouse) or alongside (human) the dotplots. Mouse intron 7, which contributes to a proportion of splice variant transcripts, is shown as a white box. Exon 4, the most conserved region, is shown in blue on the schematic and encircled in blue on the dotplot. The region of inversion is indicated with red bracketed arrows and encircled in red on the dotplot. Note the extended homology over the whole region of the inversion. (B) A schematic representation of the previously targeted Xist allele with a deletion of exon 4 (XistΔex4) (Caparros et al., 2002) and the pNBXT1 targeting construct. Conserved repetitive elements A-F within exons 1 and 7 are shown as shaded boxes. LoxP sequences (grey triangles) flank a Pgk promoter-driven neomycin (neo) selection cassette (pale grey rectangle) between 5′ and 3′ arms of homology (dark grey rectangles). The positions of the arms of homology are indicated with black lines below the schematic. A diptheria-toxin A negative selection cassette (white rectangle) was included in the targeting construct. (C) The resulting homologous recombinant allele (Xistneo) carrying both a deletion of Xist exon 4 (replaced by a LoxP sequence) and a floxed neo cassette in reverse orientation. (D) Transient expression of Cre-recombinase generates a deletion of the neo cassette (XistΔneo) and/or inversion (XistINV) of the region between exon 1 and intron 4 (5947 bp to 13,670 bp downstream of the transcriptional start site).