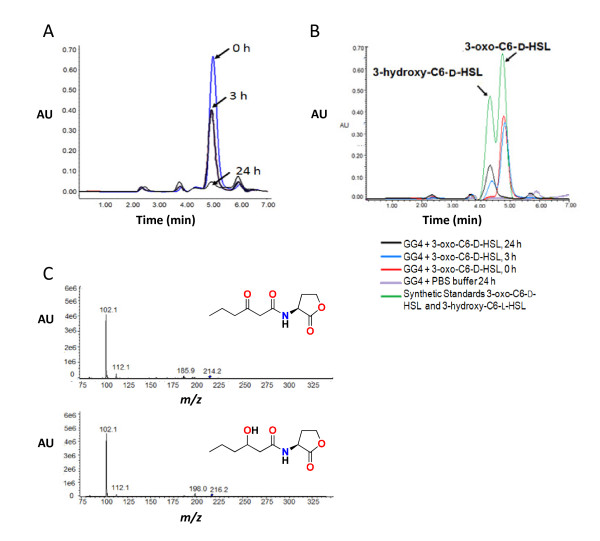
Figure 2.
HPLC analysis of the degradation of 3-oxo-C6-D-HSL after incubation with Acinetobacter GG2 and Burkholderia GG4. (A) The D-isomer of 3-oxo-C6-HSL was incubated for 0- (blue line), 3- (black line) and 24 h (grey line) with GG2, the culture supernatant extracted with ethyl acetate and subjected to HPLC analysis. The data show the disappearance of the AHL peak at 5.0 min after 24 h incubation. (B) When incubated with GG4 over a period from 0- (red line), 3- (blue line) and 24 h (black line), the 3-oxo-C6-D-HSL peak is replaced by a new peak at about 4.3 min which co-migrates with 3-hydroxy-C6-HSL. The controls used were synthetic 3-oxo-C6-D-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C6-D-HSL (green line) and PBS buffer incubated with GG4 for 24 h to ensure no 3-hydroxy-C6-HSL production by GG4 (purple line). (C) MS showing the presence of 3-oxo-C6-HSL at 0 h (upper panel; m/z 214.2 [M+H]) and 3-hydroxy-C6-HSL after 24 h (lower panel; m/z 216.2 [M+H]) when 3-oxo-C6-L-HSL was incubated with GG4.