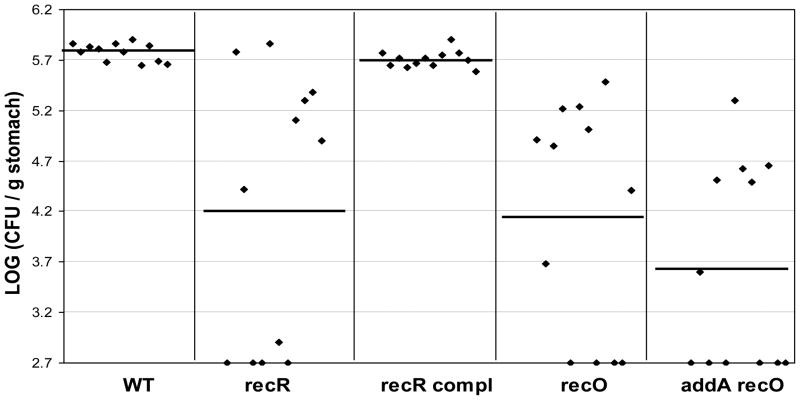
Fig. 4. Mouse colonization results for H. pylori rec mutants.
The mice were inoculated with H. pylori two times (two days apart) with a dose of 1.5 × 108 viable cells administered per animal each time. Colonization of H. pylori in mouse stomachs was examined 3 weeks after the first inoculation. Conditions were used during stomach homogenization and homogenate dilution to minimize oxygen exposure (see text). Data are presented as a scatter plot (log scale) of colony forming units per gram of stomach as determined by plate counts. Each point represents the CFU count from one mouse stomach, and the solid horizontal lines represent the geometric means of the colonization numbers for each group. The base line [log10 (CFU/g) =2.7] is the detection limit of the assay, which represents a count below 500 CFU/g stomach.