Figure 4. Using neural stem cells for drug delivery to CNS.
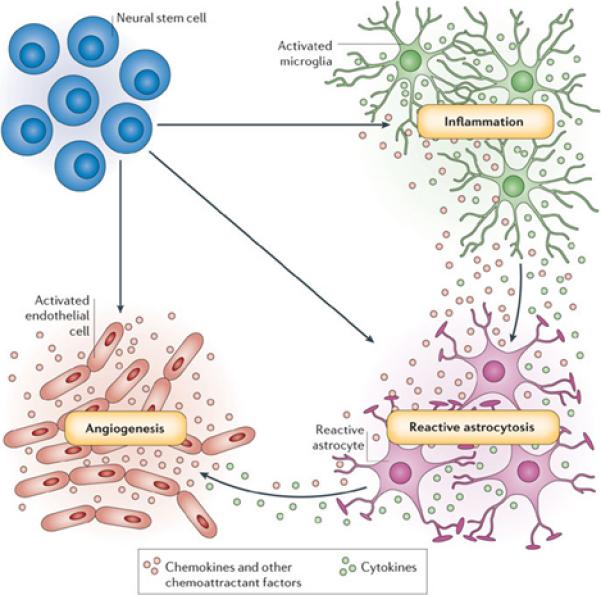
Neural stem cells are attracted by at least three physiological processes that are common to many brain pathologies: inflammation, reactive astrocytosis and angiogenesis. Pathology-induced CNS inflammation is mediated by activated microglia that release cytokines and chemokines, which, in turn, increases the inflammatory reaction. The brain lesion and subsequent inflammation trigger reactive astrocytosis. The lesion-induced angiogenesis and inflammation-activated endothelial cells enhance neural stem cell homing to brain pathology by secreting chemoattractant factors, and also offer an atypical, perivascular niche for support of immigrating neural stem cells. Used with permission 66.
