Figure 1.
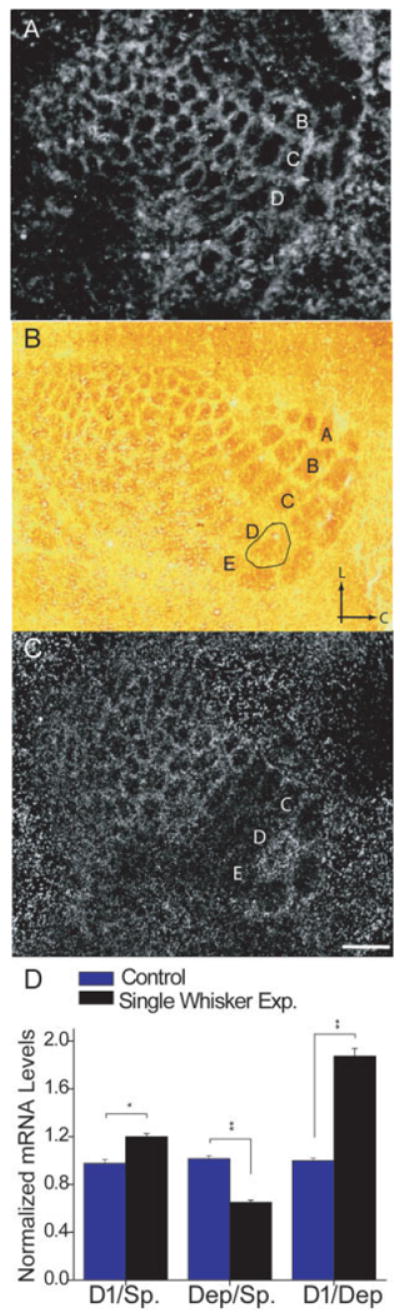
cpg15 expression in barrel cortex is regulated by single whisker experience. Representative dark-field photomicrographs of in situ hybridizations for cpg15 mRNA in mice: (A) with normal whisker experience, (C) after 12 h of single whisker experience. (B) Cytochrome oxidase staining of a section adjacent to (C) with the region representing the spared D1 whisker outlined. Arrows mark lateral (L) and caudal (C) orientation. (D) A quantitative comparison of sections such as shown in (A) and (C) (n = 8 brains per group, 2–3 sections per brain). In response to single whisker experience, cpg15 levels are increased in the barrel and septal region (barrel unit) representing the D1 whisker when compared with barrel units of the small (untrimmed in single whisker experience) whiskers in the same section (Spared), and decreased in the barrel units of the large whiskers (trimmed in single whisker experience) (Deprived). The D1/Deprived ratio represents the net change in cpg15 levels, combining the increase in the D1 barrel with the decrease in the surrounding deprived barrels. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001. Scale bar, 350 μm.
