Figure 1. EIIa/hRAMP1 transgenic mice.
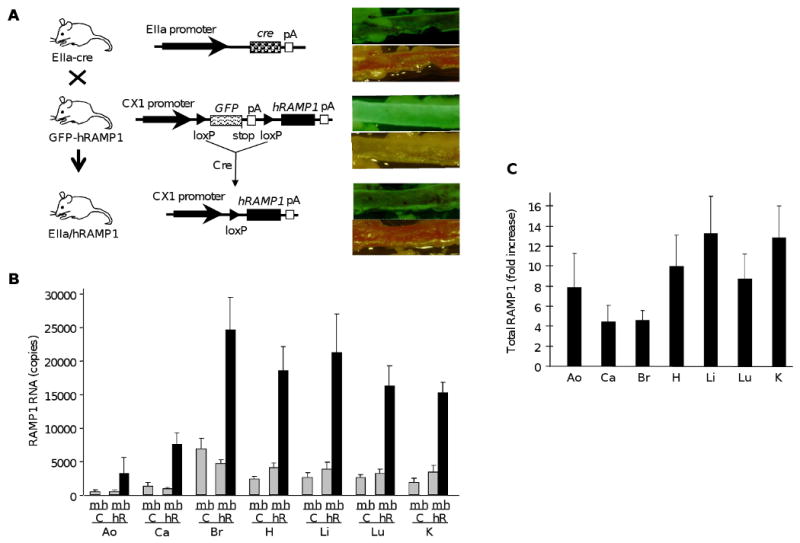
A. Strategy for producing hRAMP1 transgenic mice. Transgenic mice with the CX1 promoter and GFP–stop–hRAMP1 cassette containing a termination codon (stop) and polyadenylation signal (pA) (GFP–hRAMP1) were mated with transgenic mice with EIIa promoter driving cre recombinase (EIIa–cre). Double transgenic offspring (EIIa/hRAMP1) have cre-mediated excision of the GFP–stop sequence at the flanking loxP sites with hRAMP1 transgene expression from the CX1 promoter. Loss of GFP is shown by comparison brightfield and fluorescent images of postmortem aorta from each genotype. B. Quantitative PCR measurement of RAMP1 levels in EIIa/hRAMP1 (hR) mice and control (C) littermates. The levels of hRAMP1 (h), mRAMP1 (m) and β-actin RNA were determined by real-time PCR from aorta (Ao), carotid (Ca), brain (Br), heart (H), liver (Li), lung (Lu), and kidney (K). The copy numbers were calculated from standard curves and normalized to 50,000 copies of β-actin mRNA. Data are the mean from 3 mice in each group, with the SE from 3 independent experiments. C. Fold increase in total RAMP1 RNA levels in EIIa/hRAMP1 mice relative to control mice calculated from panel B.
