Fig. 1.
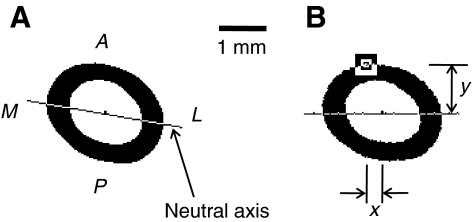
(A) Anatomical orientations and neutral axis for a hibernating 13-lined ground squirrel femur. A, M, P and L are anterior, medial, posterior and lateral anatomical directions, respectively. (B) x- and y-distances for the cortex location that is furthest from the neutral axis in the same femoral cross section. The point furthest from the neutral axis, which is the location of maximum stress in three-point bending, is indicated inside the square.