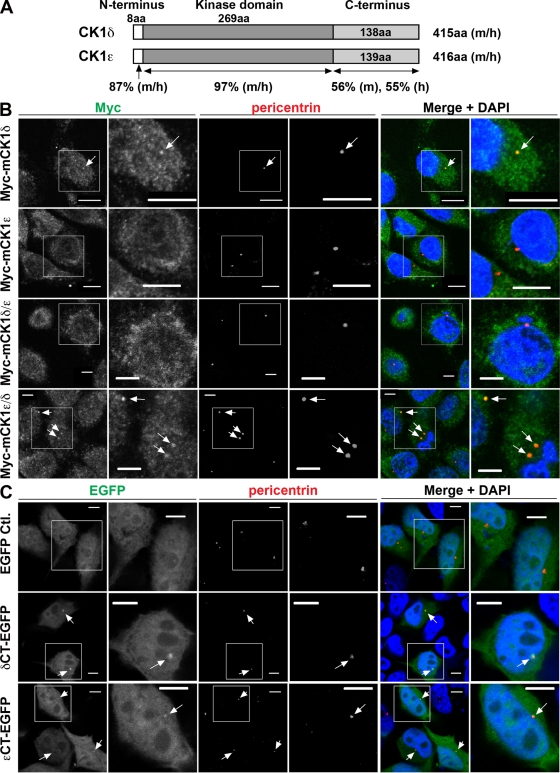
Figure 4.
C-terminal domain of CK1δ is necessary and sufficient for centrosomal localization. (A) Schematic diagram of CK1δ and CK1ε protein sequences. Numbers of amino acid (aa) residues in domains from mouse (m) and human (h) proteins are indicated along with the percent sequence identity of CK1δ and CK1ε domains in each species. Domain sequences were obtained at http://www.uniprot.org and amino acid sequence analysis was performed with resources at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/clustalw2/index.html. (B) Immunofluorescent staining of HeLa cells stably transfected with lentiviral vector encoding Myc-tagged full-length mouse CK1δ or CK1ε, or chimeras in which their C-terminal domains were interchanged (mCK1δ/ε contains the C-terminal domain of CK1ε; mCK1ε/δ contains the C-terminal domain of CK1δ). Cells were fixed in methanol, stained for Myc, pericentrin, and DNA (DAPI). Bars: (top two rows) 10 µm; (bottom two rows) 5 µm. Arrows point to colocalized signals. Magnified area corresponds to the box in adjacent panel to the left. (C) Immunofluorescent signal in HeLa cells transiently expressing EGFP, δCT-EGFP, or εCT-EGFP. Cells were fixed in formaldehyde and co-stained with pericentrin antibody and DAPI. Bars, 5 µm. Arrows point to colocalized signals. Magnified area corresponds to the box in adjacent panel to the left.