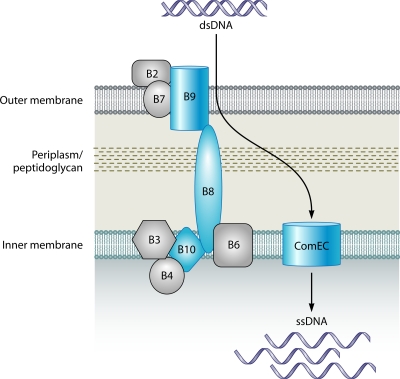
FIG. 4.
T4SS-related DNA uptake system of H. pylori and C. jejuni. The model of T4SS-mediated DNA uptake in H. pylori and C. jejuni is based on those proposed previously (261, 263, 548, 573). All components shown have been identified in H. pylori. The components also identified in C. jejuni are shown in blue (31). The transmembrane pore complex is composed of the Com proteins ComB6, ComB7, ComB8, ComB9, and ComB10. ComB3 is thought to be located in the inner membrane, but its function is unclear. Likewise, the precise function of ComB2 is not known; however, it is proposed that ComB2 forms the surface-exposed region of the T4SS. The ComB4 ATPase is thought to exist in a complex with ComB3 and may provide the energy necessary for T4SS biogenesis and/or substrate translocation. Once bound, through an unknown mechanism, donor DNA is taken up through the T4SS transmembrane complex into the periplasm. The periplasmic DNA is then processed and is likely translocated into the cytoplasm by the inner membrane-spanning channel ComEC. The processed single-stranded DNA can then be used as a substrate for homologous recombination.