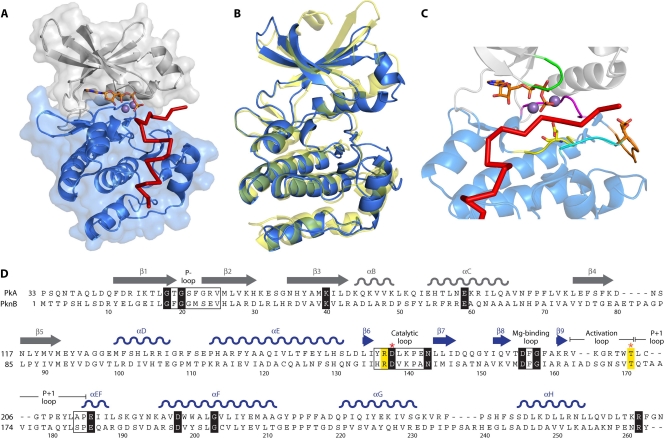
FIG. 1.
Structure of the Ser/Thr kinase catalytic domain. (A) Crystal structure of the mouse PKA catalytic domain in complex with an ATP molecule and an inhibitor peptide (Protein Data Bank [PDB] accession number 1ATP). The PKA N-terminal lobe is shown in gray, and the C-terminal lobe is shown in blue. ATP is represented as sticks, with two manganese ions shown as spheres, and the inhibitor peptide is shown as a red line. (B) Superimposition of tertiary structures of PKA and the M. tuberculosis eSTK PknB (PDB accession number 1MRU). PKA is shown in blue, and PknB is shown in yellow. (C) The regulatory elements that comprise the catalytic cleft formed between the N- and C-terminal lobes of the Ser/Thr kinase catalytic domain are indicated in the structure of PKA as follows: green, P loop; yellow, catalytic loop with the catalytic Asp residue; magenta, magnesium-binding loop; orange, activation loop with the phosphorylated Thr residue; and cyan, P+1 loop. ATP is represented as sticks, with two manganese ions shown as spheres, and the inhibitor peptide is shown as a red line. (D) Primary sequence alignment between the PKA (residues 33 to 283) and PknB (residues 1 to 266) catalytic domains. The N- and C-terminal lobes of PKA are shown in gray and blue, respectively. Conserved motifs are shown in boxes, and the invariant residues are depicted in black. Other important residues are highlighted and/or shown in bold. Red and orange asterisks indicate the catalytic Asp and phosphorylated Thr residues, respectively.