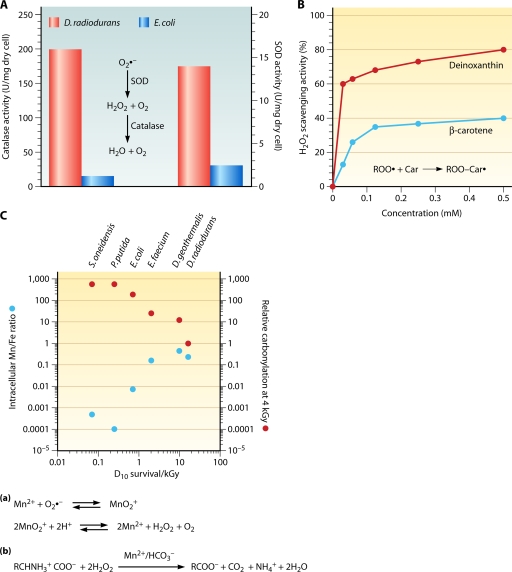
FIG. 13.
Enzymatic (A) and nonenzymatic (B and C) antioxidant defenses in D. radiodurans. (A) D. radiodurans has higher levels of catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities than does E. coli. SOD converts superoxide ions (O2·−) into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is converted by catalase into water and oxygen. (Based on data from reference 617.) (B) The D. radiodurans major carotenoid, deinoxanthin, has a higher level of H2O2-scavenging activity than does β-carotene. Carotenoids scavenge peroxyl radicals by the radical adduct formation mechanism. (Modified from reference 618 with permission from Elsevier.) (C) A high intracellular Mn/Fe ratio is correlated with a high radiation resistance level and a low protein oxidation (carbonylation) level among bacteria. Divalent manganese ions (Mn2+) can scavenge O2·− in complex with phosphates and H2O2 in complex with amino acids and bicarbonate. (Modified from reference 120 with permission of the publisher and based on data from references 36, 51, 120, 122, and 123.)