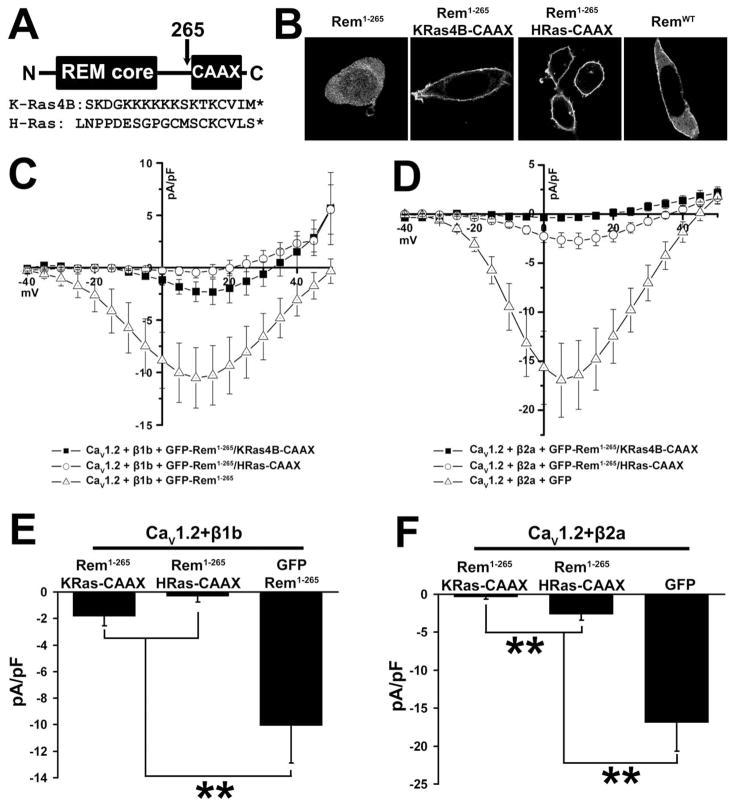
Figure 6. Membrane-targeted Rem1-265 inhibits ICa.
(A) Diagram showing construction of CAAX chimeric proteins and sequences of the K-Ras4B and H-Ras C-terminal and CAAX domains. (B) TsA201 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing GFP-Rem1-265, GFP-Rem1-265/KRas4B-CAAX, GFP-Rem1-265/HRas-CAAX, or GFP-RemWT. 72 h after transfection cells were observed by confocal microscopy. Rem1-265 shows cytosolic localization, but fusion of either of the CAAX tags results in cell peripheral distribution stronger even than that of RemWT and consistent with plasma membrane localization. (C) TsA201 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing CaV1.2, CaVβ1b, and either GFP-Rem1-265, GFP-Rem1-265/KRas4B-CAAX, or GFP-Rem1-265/HRas-CAAX. Although GFP-Rem1-265/HRas-CAAX can fully inhibit the activity of this channel complex, GFP-Rem1-265/KRas4B-CAAX shows only partial inhibition. (D) TsA201 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing CaV1.2, CaVβ2a, and either GFP-Rem1-265/KRas4B-CAAX, GFP-Rem1-265/HRas-CAAX, or GFP as a control. Although GFP-Rem1-265/KRas4B-CAAX can fully inhibit the activity of this channel complex, GFP-Rem1-265/HRas-CAAX shows only partial inhibition. (E) Currents at 5 mV from Figure 6C. A significant difference (p<0.05) between treatments is denoted by asterisks. (F) Currents at 5 mV from Figure 6D. A significant difference (p<0.05) between treatments is denoted by asterisks.