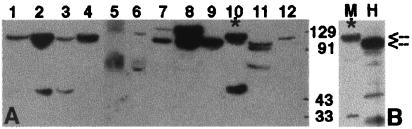
Figure 2.
Expression of the D-AKAP2 protein in various mouse tissues. (A) Mouse tissue extracts were prepared as described in Experimental Procedures; 100 μg of total protein was loaded and probed with a polyclonal antibody against D-AKAP2 (anti-D-AKAP2). Antiserum, protein A, or antigen affinity-purified antibodies gave the same result, and none of the bands were detected by a number of unrelated control antibodies. The blots shown here used protein A purified antibody against the C terminus of mouse D-AKAP2. Lanes correspond to extracts from: white adipose tissue (1), BAT (2), skeletal muscle (3), tongue (4), small intestine (5), kidney (6), lung (7), brain (8), pancreas (9), heart (10), spleen (11), and liver (12). (B) Comparison of mouse and human full-length D-AKAP2. Human D-AKAP2 was in vitro translated by using a expression vector containing the cDNA as described in Experimental Procedures. It was then loaded onto SDS-PAGE along with a sample of mouse heart extract and probed with anti-D-AKAP2. M, mouse; H, human. The two arrows indicate the mobilities of the two full-length proteins. Lane 10 and M correspond to the same extract (*).