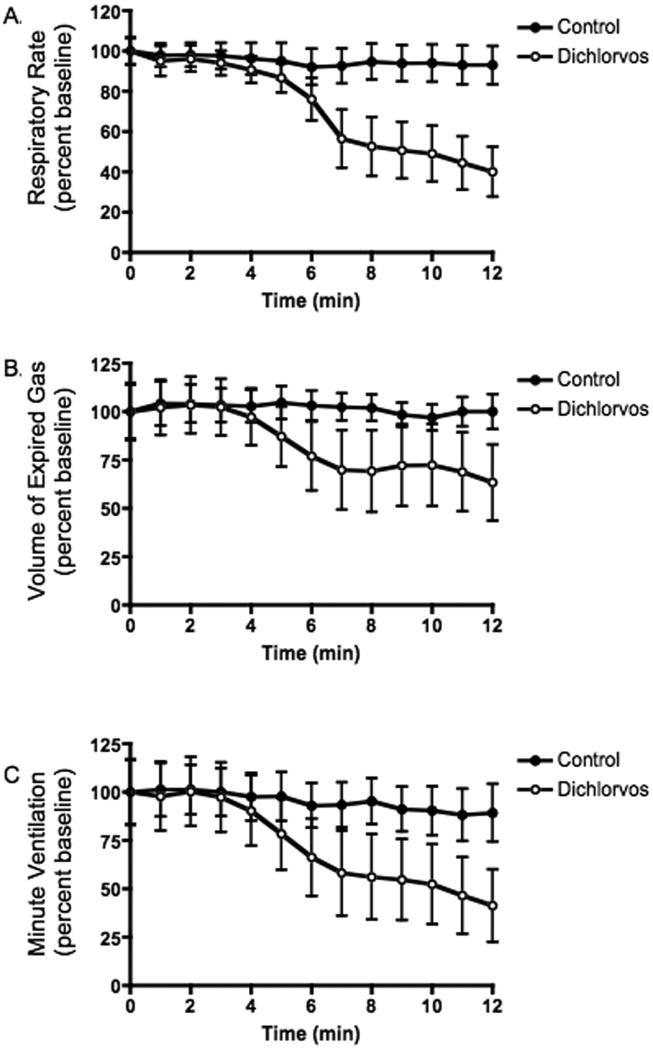
Figure 2. ABC- Respiratory rate, volume of expired gas and minute ventilation post dialysis of dichlorvos and vehicle into the ventral medulla.
Microdialysis of dichlorvos was initiated at time zero. Data represent an average of all experimental (dichlorvos) animals (open circles, n=7) and control (vehicle only) animals (filled circles, n=6). All respiratory measurements decreased significantly post exposure (p<0.0001, repeated measures ANOVA). The respiratory rate (A) and volume of expired gas (B) were significantly different, comparing dichlorvos with vehicle alone (p<0.04, ANOVA). There was no significant difference in minute ventilation (C) between groups (p=0.12, ANOVA).