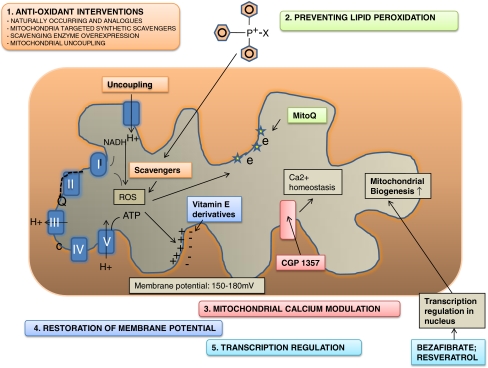
Fig. 1.
Metabolic manipulation strategies. The mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system consists of five complexes (I–V; blue). Electrons are transported (broken line) through complex I and II to complex III via Co-enzyme Q10 (Q) and to complex IV via cytochrome oxidase (c), creating a proton gradient (for schematic purposes only proton transport at complex III is depicted). This gradient is the driving force behind the production of ATP by complex V. When gene mutations or secondary dysfunction causes failure in the electron transport chain, increased oxidative stress is thought to be one of the consequences. We describe five approaches which may correct the proposed cell biological consequences. Prevention of oxidative damage (1; orange) can be achieved by either stimulating or over expressing naturally occurring antioxidants, or by scavenger supplementation. To facilitate membrane transport several triphenylphosphonium-based compounds such as TTP-vitE have been generated. Uncoupling of the respiratory chain leads to reduced oxidative damage, but also to a reduced membrane potential. Since oxidative damage is thought to cause lipid peroxidation substances preventing lipid peroxidation were designed (2; green), e.g., MitoQ. Restoring the disturbed calcium homeostasis (3; pink) has been achieved on a cellular level by CGP 1357, a benzothiazepine drug inhibiting the mitochondrial sodium/calcium (Na+/Ca2+) exchanger. The mitochondrial membrane potential (4; blue) a key indicator of mitochondrial health, can be restored by the vitamin E derivates. Finally, transcription up-regulation (5; turquoise) of genes involved in cellular energy metabolism and subsequent mitochondrial biogenesis is achieved by over expressing the transcription factor PGC1A. NADH Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced form); Q/COQ co-enzyme Q10; c cytochrome oxidase; SOD superoxide dismutase; vit E vitamin E; CGP 1357 a benzothiazepine drug inhibiting the mitochondrial sodium/calcium (Na+/Ca2+) exchanger; PGC-1A peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR-Γ) coactivator 1α; MitoQ TTP with co-enzyme Q10 attached; ATP adenosine triphospate; Ca2+ calcium; e electron