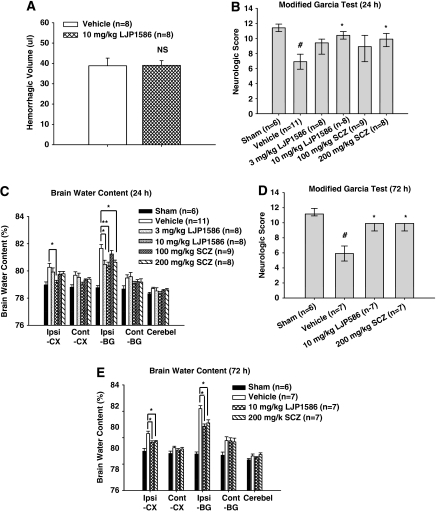
Figure 2.
Effect of vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1) inhibitors, LJP1586 and semicarbazide (SCZ) on hemorrhagic volume, neurologic score, and brain water content at 24 and 72 hours after collagenase-intracerebral hemorrhage (cICH) in mice. (A) Result of hemoglobin assay for hemorrhagic volume in vehicle (n=8) and LJP1586 (10 mg/kg)-treated mice (n=8). NS, nonsignificant. (B) The neurologic score for the modified Garcia test (healthy animal: 12) at 24 hours in sham, ICH, and ICH with treatments (LJP1586: 3 and 10 mg/kg; SCZ: 100 and 200 mg/kg). (C) VAP-1 inhibitors, LJP1586 and SCZ reduced brain water content at 24 hours after cICH in mice. Brain samples were collected from sham, ICH, and ICH with treatments (LJP1586: 3 and 10 mg/kg; SCZ: 100 and 200 mg/kg). (D) The neurologic score for the modified Garcia test (healthy animal: 12) at 72 hours in sham, ICH, and ICH with treatments (LJP1586:10 mg/kg; SCZ: 200 mg/kg). (E) VAP-1 inhibitors, LJP1586 and SCZ reduced brain water content at 72 hours after cICH in mice. Brain samples were collected from sham, ICH, and ICH with treatments (LJP1586: 10 mg/kg; SCZ: 200 mg/kg). Brain sections (4 mm) were divided into four parts: ipsilateral basal ganglia (Ipsi-BG), ipsilateral cortex (Ipsi-CX), contralateral basal ganglia (Cont-BG), and contralateral cortex (Cont-CX). Cerebellum (Cerebel) is the internal control. #P<0.05 versus sham group. *P<0.05 versus vehicle group. **P<0.01 versus vehicle group.