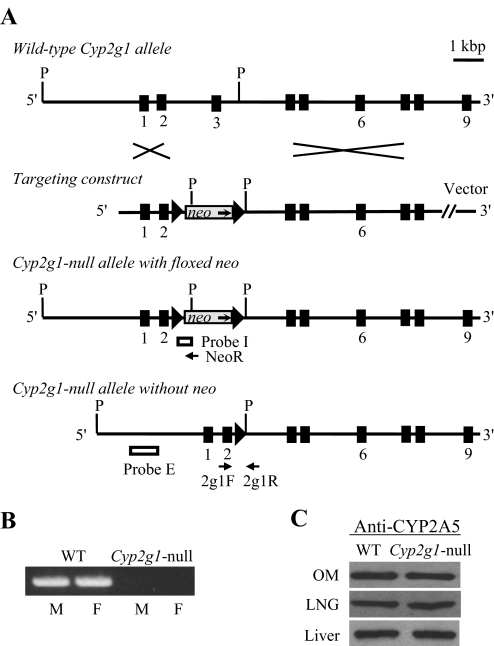
Fig. 1.
Targeted disruption of the mouse Cyp2g1 gene. A, structures of the WT Cyp2g1 allele, the targeting vector, the Cyp2g1 allele with a floxed neo insertion, and the Cyp2g1 allele without neo. Positions of the PCR primers (2g1F, 2g1R, and NeoR) used for genotyping, as well as the Pst I restriction sites (P) and the external (Probe E) and internal (Probe I) probes used for Southern blot analysis, are indicated. Triangles represent loxP sites; selected exons are numbered below. B, absence of CYP2G1 expression in the Cyp2g1-null mice. RNA-PCR was performed using total RNA prepared from the olfactory mucosa of adult male (M) or female (F) WT B6 or Cyp2g1-null mice. PCR products were analyzed on an agarose gel and visualized by staining with ethidium bromide. C, normal CYP2A5 expression in the Cyp2g1-null mice. Immunoblot analysis was performed for microsomal proteins (5 μg per lane for LNG and 1 μg per lane for olfactory mucosa and liver) of the WT B6 and Cyp2g1-null mice, with use of an anti-CYP2A5 antibody. Microsomes were prepared from pooled olfactory mucosa, LNG, or liver from five male mice (2 months old). Densitometric analysis (not shown) indicated that the maximal difference in band intensity between samples from WT and the Cyp2g1-null groups was less than 10%. Typical results are shown.