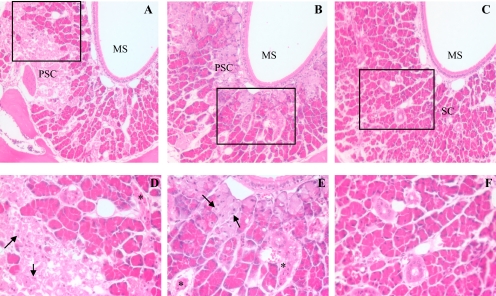
Fig. 2.
Histological analysis of APAP toxicity in the LNG. Male, 2-month-old B6 WT, Cyp2g1-null, and Cyp2a5-null mice (eight in each group) were treated, at 9:00 to 10:00 AM after overnight fasting, with a single injection of APAP (400 mg/kg i.p.) in warm saline. Control groups (not shown) received the vehicle only. Mice were killed at 24 h after the APAP injection. All sections were at the level of the second palatal ridge (level 5 in Young, 1981). Typical images are shown, at either 100× (A–C) or 400× (D–F, for boxed area only) magnification. LNG in APAP-treated WT (A) and Cyp2g1-null (B) mice exhibited extensive cell necrosis, as indicated by the widespread appearance of pale, ragged secretory cells (PSC) and dark, shrunken duct cells (*), and apoptotic glandular epithelial cells (arrows); LNG in APAP-treated Cyp2a5-null mouse (C) had normal, palely staining duct cells with open face nuclei and plump secretary cells (SC) with bright eosinophilic cytoplasmic granules. MS, maxillary sinus.