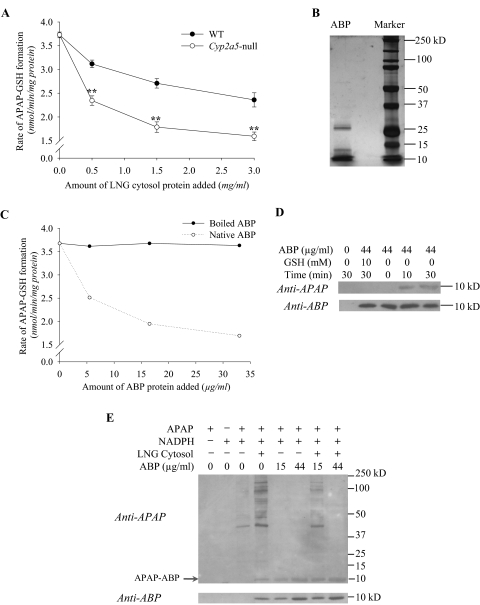
Fig. 6.
Ability of ABP to compete with GSH and cellular proteins for adduction with APAP in vitro. Reaction mixtures contained 100 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.6, 0.5 mM APAP, 0.5 mg/ml olfactory mucosa microsomal protein of 2- to 3-month-old male B6 WT mice, and other components as indicated. Unless otherwise indicated, reactions were carried out for 10 min at 37°C. A, differential inhibition of APAP-GSH formation by LNG cytosol preparation from WT and Cyp2a5-null mice. Rates of in vitro formation of APAP-GSH were determined in the presence of 1.0 mM NADPH, 0.2 mM GSH, and increasing amounts of LNG cytosolic protein (0–3 mg/ml), prepared from 2-month-old male WT or Cyp2a5-null mice. The values presented are means ± S.D. (n = 3); ** P < 0.01, Student's t test. In negative control reactions, the addition of boiled LNG cytosol preparation from 2-month-old male WT mice (at 3 mg/ml) did not affect rates of APAP-GSH formation (data not shown). B, gel-electrophoretic analysis and silver staining of partially purified ABP protein. A preparation of ABP (∼2 μg of protein) purified from mouse saliva was analyzed under reducing condition on a 10% polyacrylamide gel. Selected fragments of a prestained protein size marker are labeled. C, inhibition of APAP-GSH formation by purified ABP. Rates of formation of APAP-GSH were determined in the presence of 1.0 mM NADPH, 0.2 mM GSH, and increasing amounts of either boiled or native ABP (at 0–33 μg/ml; amounts equivalent to those of ABP present in 0 to 3 mg/ml LNG cytosol protein from Cyp2a5-null mice). The values presented are averages for duplicated samples at each ABP concentration. D, time-dependent formation of APAP-ABP protein adduct in vitro. Reactions were carried out for 0 to 30 min in the presence of 1.0 mM NADPH, 0 or 44 μg/ml ABP, and 0 or 10 mM GSH. Aliquots of the reaction mixtures, equivalent to 5 μg of the olfactory mucosa microsomal protein per lane, were analyzed on immunoblots, with use of either an anti-APAP or an anti-ABP. E, Competition between ABP and other LNG cytosolic proteins for adduction with APAP. Reactions were performed as in C, except that LNG cytosol preparation from Cyp2a5-null mice was added at 1.5 mg/ml, whereas the concentration of ABP varied between 0 and 44 μg/ml. Addition of ABP to reactions containing LNG cytosol led to increases in the abundance of APAP-ABP, and decreases in the abundance of the other APAP-protein adducts.