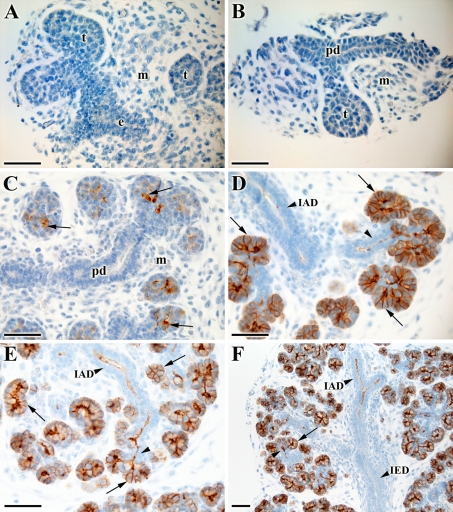
Fig. 1.
AQP5 expression pattern during prenatal development of the mouse submandibular gland (SMG). A Pseudoglandular stage (~E14): no AQP5 staining is detectable in the terminal bud (t), epithelial stalk (e) or mesechyme (m). B Early canalicular stage (~E14-15): AQP5 negative cells in the terminal bud (t), presumptive duct (pd), and mesenchyme (m). C Late canalicular stage (~E15-E16): scattered positive pro-acinar cells are present (arrow). No AQP5 is found in the presumptive duct (pd) or mesenchyme (m). D Early terminal bud stage (~E16-E17): all pro-acinar cells are AQP5 positive (arrow). In the intralobular duct (IAD), cells proximal to the pro-acini show apical AQP5 staining (arrowhead). E and F Late terminal bud stage (~E17-18): a similar expression pattern is observed as in D. Additionally, the rest of the intralobular duct (IAD) is also positive, and the interlobular duct (IED) is negative. Scale bar (A–E) 50 μm and (F) 100 μm