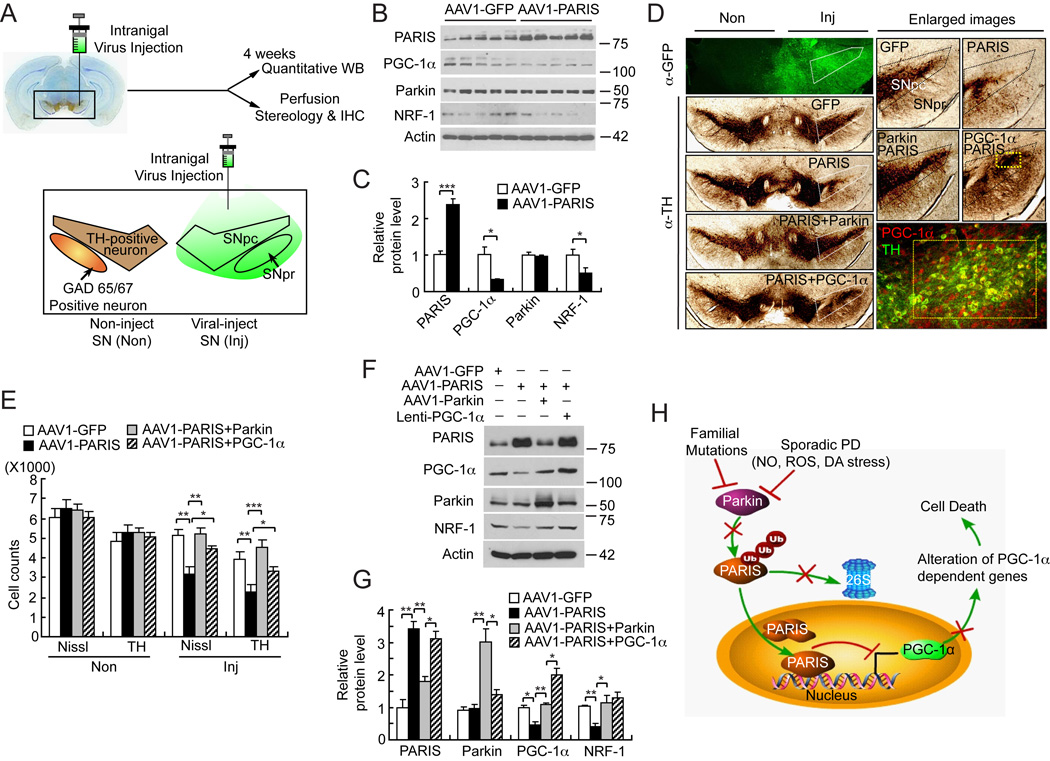
Figure 7. Introduction of AAV1-Parkin or Lenti-PGC-1α in mice SN protects from AAV1-PARIS-mediated selective dopaminergic neuronal toxicity.
(A) Schematic illustration of intranigral viral injection and transduced brain regions.
(B) Immunoblot analysis of PARIS, PGC-1α, parkin and NRF-1 four-weeks post intranigral injection of AAV1-PARIS, n = 5 per group.
(C) Quantitation of the immunoblots in panel B normalized to β-actin.
(D) TH staining of a representative section of mice injected with AAV1-GFP, AAV1-PARIS ± AAV1-parkin or AAV1-PARIS ± Lenti-PGC-1α. Each panel shows the noninjected side (Non) and contralateral injected side (Inj) and white pentagonal box indicates the SNpc. Enlarged images containing SNpc and SNpr are shown on the right panels. AAV1 encoding GFP was used as transduction control in all injection procedures. Broad regions including SNpc and SNpr were successfully transduced (left top panel). In right bottom panel, yellow rectangle indicates the region that PARIS and lenti- PGC-1α co-transduced. Approximately 30% of the SNpc was transduced with lenti-PGC-1α and this is the region, which is protected from PARIS toxicity, n = 6 per group.
(E) Stereological TH, Nissl-positive neuronal counting, n = 6 per group.
(F) Immunoblot analysis of PARIS, PGC-1α, parkin and NRF-1, n = 3.
(G) Quantitation of the immunoblots in panel F normalized to β-actin.
(H) Parkin-PARIS-PGC-1α pathway as a model in PD. Endogenous PARIS acts to maintain the balance of PGC-1α levels. In PD, parkin is inactivated by diverse insults such as familial mutations, reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitrosative (NO) and dopamine (DA) stress and PARIS accumulates. Accumulated PARIS continuously inhibits PGC-1α transcription leading to reduction in PGC-1α dependent genes. Ultimately this situation results in neurodegeneration in PD. Data = mean ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ANOVA with the Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test.
See also Figure S6.