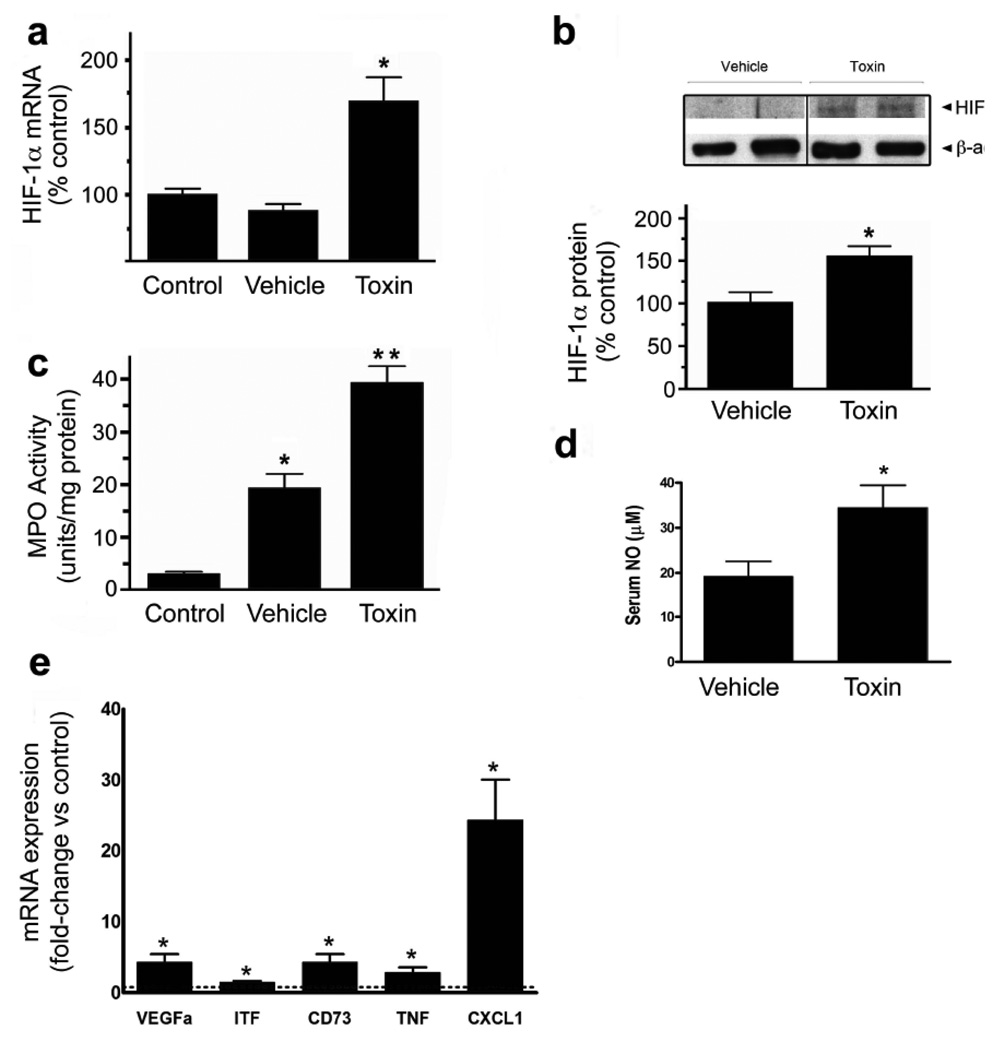
Figure 5.
C.difficile toxin increases HIF-1α expression and induces inflammation in an in vivo model of CDAD. (a) HIF-1α mRNA levels were measured with qPCR in ileum isolated from control animals (no surgery), mice with ileal loop treated with vehicle or exposed to 100µg of C.difficile toxin in the ileal loop (*p<0.05 compared to control and vehicle, n=5). (b) HIF-1α protein was assessed in ileal tissue isolated from mice treated with vehicle or C.difficile toxin (100µg), *p<0.05 compared to vehicle, n=4 (NB100-105). (c) Tissue inflammation (MPO levels) was assessed in ileum isolated from control animals (no surgery) and mice treated with vehicle or C.difficile toxin (100µg), *p<0.05 compared to control and vehicle, **p<0.05 compared to vehicle, n=9. (d) Serum NO levels were assessed from mice treated with either vehicle or C.difficile toxin (100µg), *p<0.05 compared to vehicle, n=9. (e) qPCR was performed on RNA isolated from vehicle and toxin-treated ileal loops. Data is expressed as fold-change relative to control where 1 is equal to expression in the control group (dashed line). *p<0.05 compared to control, n=3.