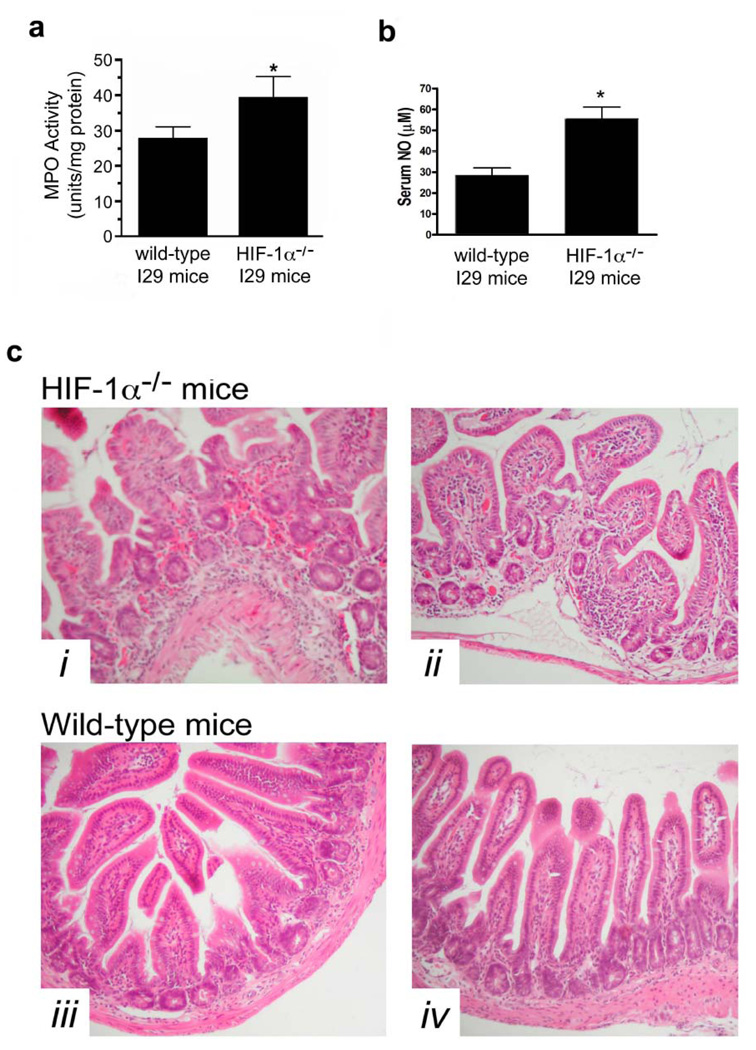
Figure 6.
Targeted deletion of HIF-1α in intestinal epithelium augments C.difficile toxin-induced inflammation. (a) Tissue inflammation as assessed by MPO levels in ileum isolated from wild-type I29 and HIF-1α epithelial-targeted knockout (HIF-1α−/−) mice treated with C.difficile toxin (100µg), *p<0.05 compared to wild-type I29, n=6. (b) Serum NO levels were assessed from wild-type I29 and HIF-1α epithelial-targeted knockout (HIF-1α−/−) mice treated with C.difficile toxin (100µg), *p<0.05 compared to wild-type I29, n=6. (c) H&E stained ileal sections from HIF-1α−/− (top row) and wild-type I29 (bottom row) following 4h exposure to C.difficile toxin (100µg).