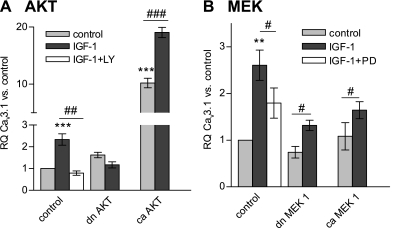
Fig. 2.
Effect of signaling pathways activated by IGF-I on Cav3.1 upregulation. A: constitutively active (ca, n = 4) and dominant-negative (dn, n = 4) protein kinase B (Akt) isoforms were overexpressed in cultured rat PASMCs using adenovirus constructs. Forty-eight hours after infection, PASMCs were stimulated with 100 ng/ml IGF-I for another 48 h and then harvested for RNA purification (n = 3). RQ of Cav3.1 mRNA was calculated vs. control (β-galactosidase adenovirus infected, unstimulated) cells. The role of Akt activation in IGF-I-induced Cav3.1 upregulation was also tested by blocking the pathway with 10 μM LY-294002 (n = 4). B: ca (n = 4) and dn (n = 4) MEK1 isoforms were overexpressed in cultured rat PASMCs, which were then exposed to 100 ng/ml IGF-I for an additional 48 h. The role of ERK1/2 activation in IGF-I-induced Cav3.1 mRNA upregulation was also tested by blocking ERK1/2 with 10 μM PD-98059 (n = 4). Values are means ± SE. Statistical significance is calculated using paired t-test on dCt values. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control (infected, unstimulated) PASMCs. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 reflect the effect of the inhibitory action on IGF-I stimulation.