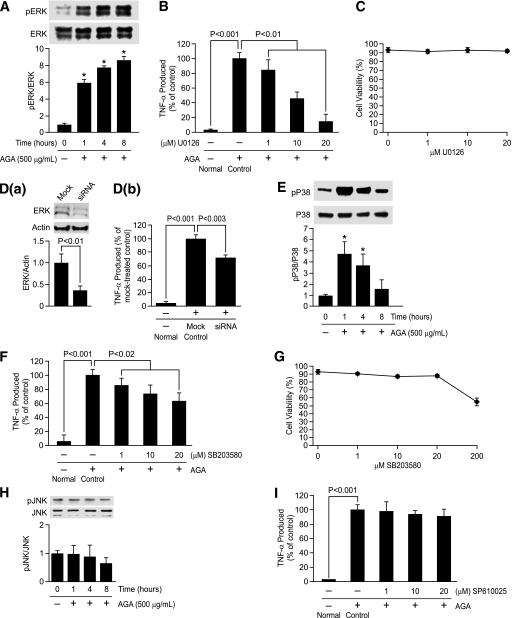
FIG. 4.
Phosphorylation of ERK and P38, but not JNK, causes TNF-α release in the activated retinal microglial cells. A: Time-dependent, AGA-induced activation of ERK in retinal microglial cells. Cells were treated with 500 μg/mL AGA for 1–8 h. Phospho (p)ERK and its total protein in cell lysate were determined by Western analysis. Ratios of the intensities of phospho-proteins relative to total proteins for each time point were compared with control, which was arbitrarily set at 1.0. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three experiments (*P < 0.001). B: Dose-dependent inhibition of AGA-induced TNF-α release in retinal microglial cells by inhibitor for ERK (U0126). Cells were treated with 500 μg/mL of AGA for 4 h in the presence of indicated concentrations of inhibitor. TNF-α levels were compared with the vehicle-treated control. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three to five experiments. C: U0126 also had no effect on cell viability, as determined by trypan blue exclusion test. D: Inhibition of AGA-induced TNF-α release by ERK siRNA in retinal microglial cells. Cells were transfected with siRNA or scrambled siRNA for 48 h and then treated with AGA for 4 h. a, Measurement of ERK expression relative to actin by Western blot after transfection with anti-ERK siRNA. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three experiments. b, ELISA-measured TNF-α levels were compared with the scrambled siRNA-transfected control. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three experiments. E and H: Time-dependent, AGA-induced activation of P38 and JNK in retinal microglial cells. Cells were treated with 500 μg/mL AGA for 1–8 h. Phospho (p)P38, pJNK, and its total proteins in cell lysates were determined by Western analysis. Ratios of the intensities of phospho-proteins relative to total proteins for each time points were compared with control, which was arbitrarily set at 1.0. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three experiments (*P < 0.001). F and I: Dose-dependent inhibition of AGA-induced TNF-α release in retinal microglial cells by inhibitors for P38 (SB203580) and JNK (SP610025). Cells were treated with 500 μg/mL of AGA for 4 h in the presence of indicated concentrations of inhibitors. TNF-α levels were compared with the vehicle-treated control. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three to five experiments. G: Effect of SB203580 on cell viability, as determined by trypan blue exclusion test.