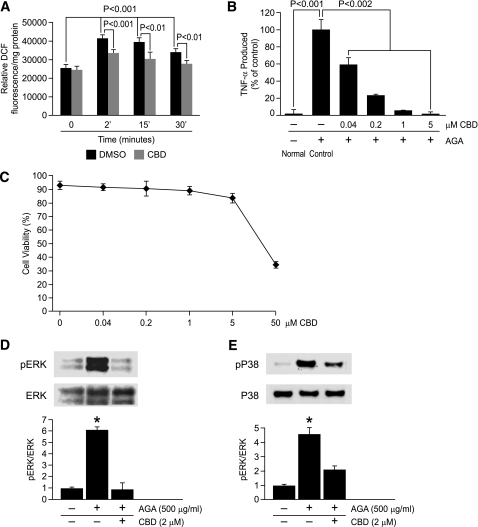
FIG. 6.
ROS formation is an early event involved in AGA-induced TNF-α release and MAPKs activation in retinal microglial cells. A: AGA-induced, time-dependent ROS formation in retinal microglial cells. ROS formation was prevented by pretreatment with CBD (2 μmol/L). Retinal microglial cells loaded with 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate were pretreated with CBD or DMSO for 60 min and treated with AGA, and the fluorescence of DCF was measured at 0, 2, 15, or 30 min. ROS formation was expressed as changes in DCF fluorescence/mg protein. Data shown are the mean ± SD of six experiments. B: Dose-dependent inhibition of AGA-induced TNF-α release in retinal microglial cells by CBD. Cells were treated with 500 μg/mL of AGA for 4 h in the presence of indicated concentrations of CBD. TNF-α levels were compared with the vehicle-treated control. C: Effect of CBD on cell viability, as determined by trypan blue exclusion test. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three experiments. D and E: CBD inhibits AGA-induced MAPKs activation in retinal microglial cells. Cells were treated with vehicle or CBD 30 min before AGA treatment for 4 h. Phospho-ERK, total ERK, phospho-P38, and total P38 MAPK were determined by Western blot and quantified by densitometric analyses. Each AGA-treated sample with or without inhibitors was compared with the untreated sample, set as 1.0. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three experiments. *P < 0.001.