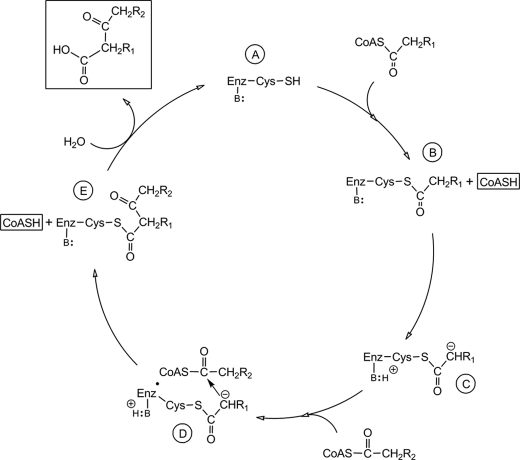
FIGURE 7.
Proposed reaction cycle for OleA. The top of the cycle (A) shows the resting enzyme that reacts with an acyl-CoA to start the reaction cycle; B, enzyme with the covalently attached acyl chain; C, enzyme having abstracted a proton from the acyl chain to activate it; D, activated acyl chain reacting with the second acyl chain bound to the enzyme; E, condensed fatty acyl chains still bonded to the enzyme system just prior to hydrolytic release. CoASC(O)CH2R1 and CoASC(O)CH2R2, first and second reacting acyl-coenzyme A, respectively. B: attached by a line to Enz represents an enzyme base. The products of the reaction, two molecules of coenzyme A (CoASH) and a β-keto acid, are highlighted by boxes.