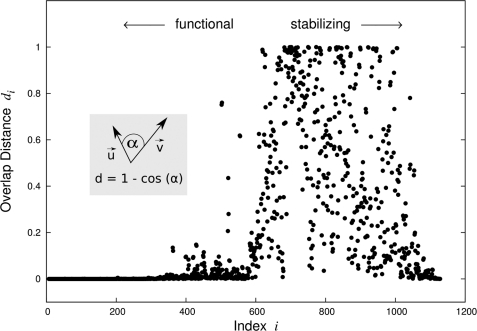
FIGURE 7.
Overlap distance for eigenvectors of the wild type and mutant (Δ 30–83) Kcv. With αij denoting the angle between two eigenvectors, ui (wild-type) and vi (mutant), the overlap distance is computed as dij = 1-cos(αij). Overlap distances are shown for corresponding eigenvectors computed for the wild-type and the mutant system using anisotropic network models. In the mutant Kcv, the contact between residues 30 and 83 is artificially deleted within all chains simultaneously. Small indices (slow motions) agree with a high confidence between the wild type and mutant. The respective eigenvectors describe global motions of the molecule that are relevant for biological function(s). High-frequency motions (large indices), however, describe localized dynamics acting on single atoms crucial for the stability of the protein (46). We clearly see that most if not all changes that are caused by the mutation Δ 30–83 stem from the structural modes and thus cause stability issues.