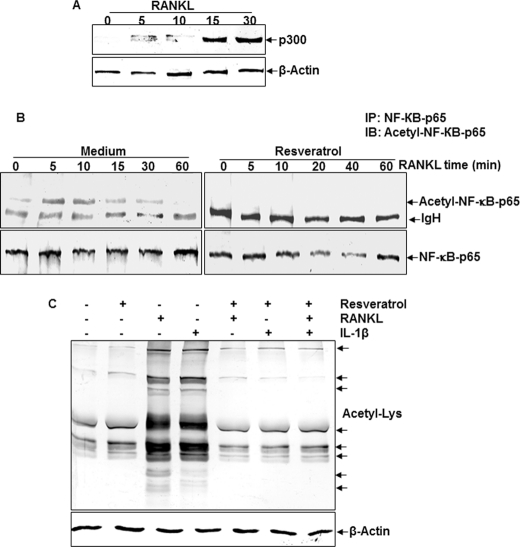
FIGURE 7.
Analysis of RANKL-mediated p300 expression and resveratrol-mediated inhibition of RANKL-dependent p65 acetylation in bone-derived cells. A, detection of p300 expression. Bone-derived cells (1 × 106 cells) in monolayer culture were incubated with RANKL (10 nm) for the indicated times and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-p300 antibody or anti-actin antibody (control). B, effect of resveratrol on RANKL-induced acetylation of p65. Cells were treated with 5 μm resveratrol for 4 h and then exposed to 10 nm RANKL. Whole cell extracts were prepared, immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-p65 antibody, and subjected to Western blot analysis using an anti-acetyl-lysine antibody. The same blots were reprobed with an antibody to anti-p65. C, effect of resveratrol on RANKL- or IL-1β-induced protein acetylation. Cells were treated with 5 μm resveratrol for 4 h and then exposed to 10 nm RANK or 10 ng/ml IL-1β for 20 min. Whole cell extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis using an anti-acetyl-lysine antibody.