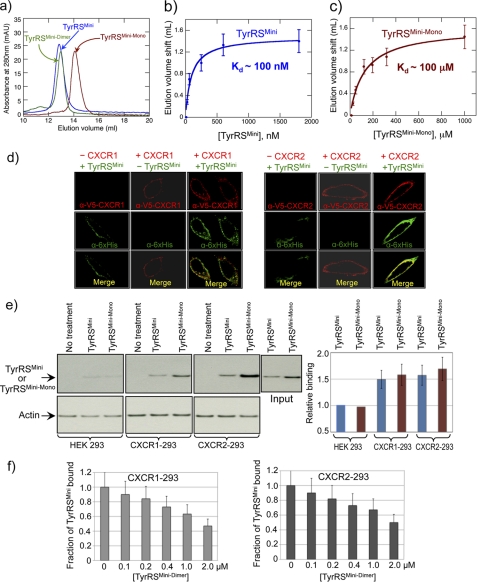
FIGURE 2.
Determination of dimer-monomer equilibrium dissociation constants for WT and Δ159–161 TyrRSMini. a, analytical gel chromatography of WT, Δ159–161, and T130COX His6-tagged TyrRSMini. WT and T130COX peaks correspond to dimeric TyrRSMini (named TyrRSMini-Dimer), and Δ159–161 peak corresponds to monomeric TyrRSMini (named TyrRSMini-Mono). maU, milliabsorbance units. b and c, estimation of dimer-monomer equilibrium dissociation constant for WT TyrRSMini (b) or TyrRSMini-Mono (c) by gel filtration chromatography in combination with immunoblotting. Error bars correspond to mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. d, TyrRSMini binds to CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors transiently expressed in HeLa cells with V5-tagged CXCR1/2. Cells were fixed and doubly stained with anti-His6 (green) and anti-V5 (red) antibodies to detect TyrRSMini and CXCR1/2 receptors, respectively. e, TyrRSMini and TyrRSMini-Mono bind to CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors expressed in HEK 293 cells. The bar graph was generated by normalizing binding to the input of TyrRSs and amount of actin (as a measure of cell concentration) and is shown as mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments. f, TyrRSMini-Dimer competes with WT TyrRSMini for binding to CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors. CXCR1-293 and CXCR2-293 cells were incubated with 100 nm WT His6-tagged TyrRSMini or TyrRSMini-Mono at 4 °C for 1 h and then analyzed as described in the supplemental material. Data in bar graph format are shown as mean ± S.D. (n = 3 for each concentration of TyrRSMini-Dimer).