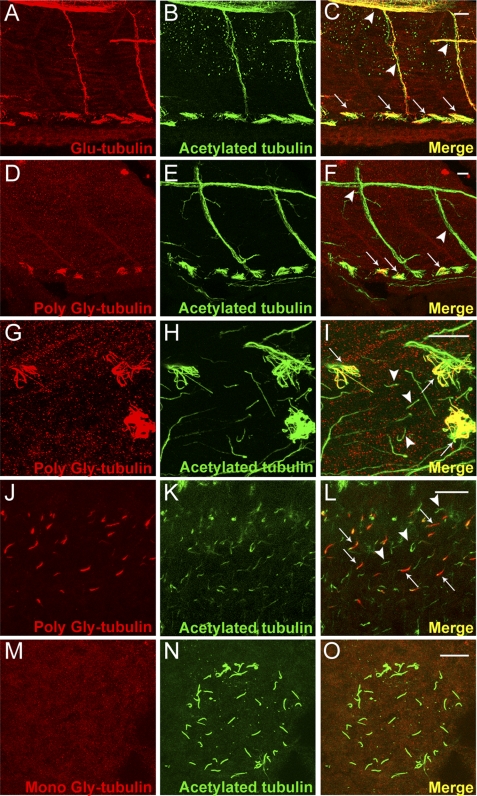
FIGURE 1.
In vivo distribution of glutamyl and glycyl-modified tubulin in zebrafish. A–C, confocal projection of the trunk region of a 2.5-day post-fertilized wild type zebrafish larva, double immunolabeled with Glu-tubulin specific mAb GT335 (red) (A), acetylated tubulin-specific mAb 6-11B-1 (B), and the merged image (C). Glutamylated and acetylated tubulin overlap in motor neurons (arrowheads in C) and all types of pronephric cilia (arrows at bottom in C). D–F, confocal projections of the trunk region of a 2.5-day post-fertilized wild type zebrafish larva double immunolabeled with poly-Gly tubulin-specific R PolyG (red) (D), acetylated tubulin specific mAb 6-11B-1 (green) (E), and the merged image (F). Poly-Gly tubulin was localized specifically in pronephric cilia (arrows) and excluded from the primary motor neurons (arrowheads). G–I, high magnification view of the pronephros showing cilia labeled with poly-Gly tubulin-specific R PolyG (G), acetylated tubulin specific 6-11B-1 (H), and the merged image (I). Polyglycylated tubulin occurred only in the multicilia subtype (arrows in I) and not in adjacent, single pronephric cilia (arrowheads in I). J–L, confocal projection of spinal canal cilia immunolabeled with poly-Gly tubulin-specific R PolyG (J) (red), acetylated tubulin-specific mAb 6-11B-1 (K) (green), and the merged image (L). Polyglycylated tubulin was present in a specific subset of cilia (arrows in L). M–O, confocal projections of the Kupffer vesicle in a 10-somite wild type zebrafish embryo, double immunolabeled with mono-Gly tubulin-specific mAb TAP952 (M); acetylated tubulin specific mAb 6-11B-1 (N), and the merged image (O). Monoglycylated tubulin was absent from all Kupffer vesicle cilia. Scale bars = 10 μm.