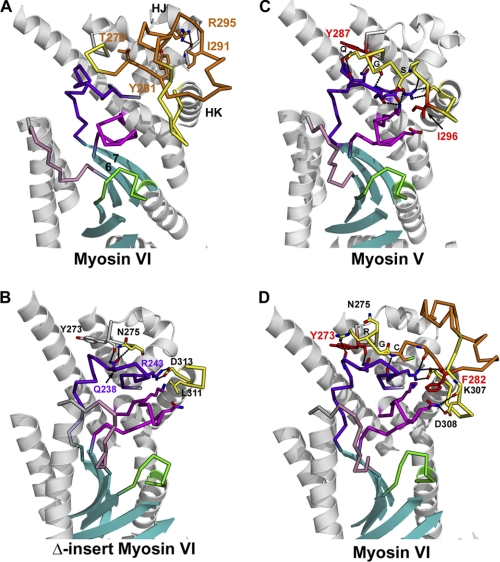
FIGURE 3.
Insert-1 interactions with the U50 subdomain and their possible influence on the dynamics necessary for transition between myosin states. Insert-1 (orange) is located in a loop (yellow) of the U50 subdomain that makes interactions with the U50 linker (dark purple) and Switch I (magenta). Note that the U50 linker and switch I are connected to the last two strands of the central β-sheet (cyan), which is part of the transducer in myosin (19) that undergoes major rearrangements upon nucleotide binding and dissociation. A, in myosin VI, insert-1 corresponds to a 26-residues insertion in the loop that connects helix HJ to helix HK. In all wild type myosin VI structural states solved to date, several conserved interactions are observed between insert-1 and the rest of the U50 subdomain and stabilize its conformation. In particular, insert-1 residues Thr-279, Tyr-281, Ile-291, Arg-295 play an anchoring role for the insert. Of note, arginine 295 plays an important role in anchoring insert-1 to the linker found between helices HI and HJ by interacting with the main chain carbonyl of Ala-255. B, in all myosin structures solved to date, including the Δ-insert-1 structure, the first residue of helix HK that follows the insert-1 loop is an aspartate (Asp-313 in myosin VI), which makes a conserved salt bridge interaction with the arginine Arg-243 of the U50 linker (dark purple). At the beginning of the loop, another conserved interaction involves the main chain carbonyl of Tyr-273 that interacts with Q238 of the U50 linker. C, in myosin V the loop (Lys-289—Asp-301; yellow) in which insert-1 is found in myosin VI makes several interactions with the U50 linker and Switch I, in particular via myosin V residues Q290 (Q), G291 (G), S293 (S), Ile-296. B, in the Δ-insert-1 structure, the main chain conformation of the loop differs from that of myosin V, although it also contains 13 residues. This results in a weakening of the interactions mediated by insert-1 residues with the U50 linker and Switch I compared with either myosin V or wild type myosin VI. D, in wild type myosin VI, the conformation of the beginning of the loop is similar to that found in myosin V, and myosin VI residues Arg-276 (R), Gly-277 (G), Cys-278 (C) interact similarly with the U50 linker as do Gln-290, Gly-291, and Ser-293 in the myosin V structure. Residue Phe-282 of insert-1 is found in similar position as Ile-296 in myosin V and also interacts with Switch I. The nature of the contacts is different in the two myosins, however, which likely influences the U50 linker dynamics and the rates of rearrangements within the transducer.