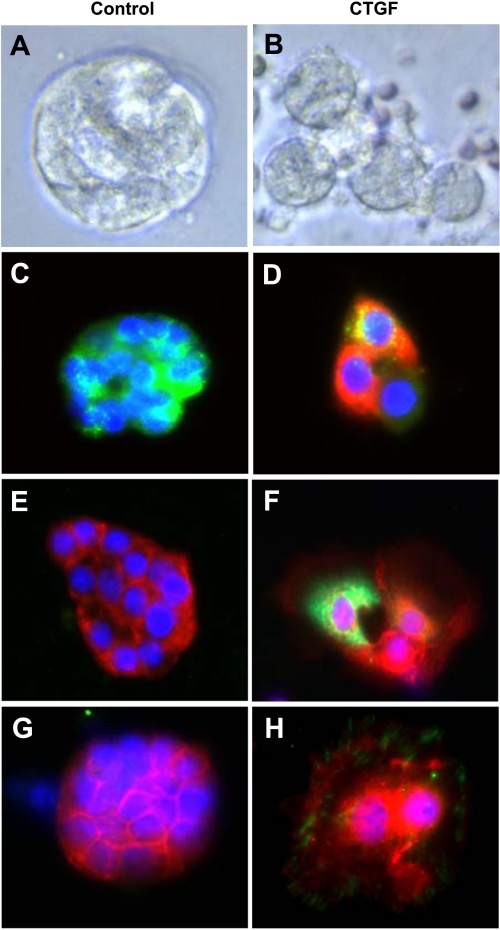
Fig. 7.
CTGF induced β-catenin nuclear translocation in primary alveolar type II epithelial (AT II) cells. AT II cells were isolated from 4-wk-old control and CTGF lungs and cultured for 72 h on Matrigel. Live cell imaging demonstrated alveolar-like cysts in control group (A) but larger and spread cells in CTGF group (B). Double immunofluorescence staining for pro-SP-C (green signal) and CTGF (red signal) and DAPI nuclear staining (blue signal) detected only pro-SP-C in control cells (C), but pro-SP-C and CTGF were colocalized (orange signal) in CTGF cells (D). Double immunofluorescence staining for β-catenin (red signal) and CTGF (green signal) and DAPI nuclear staining (blue signal) detected only β-catenin in the cytoplasm in control cells (E), but β-catenin was localized in the nuclei (pink signal) and in the cytoplasm (pale green signal) in CTGF-expressing cells (F). Double immunofluorescence staining for β-catenin (red signal) and integrin-linked kinase (ILK) (green signal) and DAPI nuclear staining (blue signal) detected only β-catenin in the cytoplasm in control cells (G), but β-catenin was localized in the nuclei (pink signal) and in the cytoplasm whereas ILK was localized in the cytoplasm in CTGF cells (H).