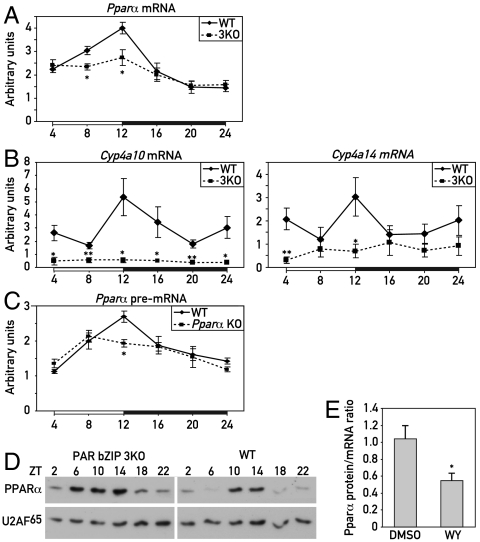
Fig. 1.
Expression of PPARα in PAR bZip 3KO mice. (A) Temporal expression of Pparα mRNA in the livers of WT and PAR bZip 3KO mice. RNA levels were estimated by real-time RT-PCR. Mean values ± SEM obtained from six animals are given. (B) Temporal expression of the PPARα target genes Cyp4a10 and Cyp4a14 in the liver of WT and PAR bZip 3KO mice, as determined by real-time RT-PCR. Mean values ± SEM obtained from six animals are given. (C) Temporal expression of Pparα pre-mRNA transcripts in the livers of WT or Pparα KO mice. A PCR amplicon located in the second intron was used in these quantitative RT-PCR experiments. Mean values ± SEM obtained from four animals are given. (D) Temporal expression of PPARα protein in liver nuclear extracts from PAR bZip 3KO and WT mice. Signals obtained with U2AF65 antibody were used as loading controls (U2AF65 is a constitutively expressed splicing factor). (E) Ratio of liver PPARα protein/Pparα mRNA levels after injection of the synthetic PPARα ligand WY14643 or its solvent (50% DMSO) in PAR bZip 3KO mice at ZT2. Mean values ± SEM obtained from six animals are given. The raw data used for these computations are presented in Fig. S3. The zeitgeber times (ZT) at which the animals were killed are indicated (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01 KO vs. WT, Student’s t test).