Fig. 4.
Change in the apparent area of an Sp vesicle caused by tube retraction when the membrane tension is increased via micropipette aspiration. The vesicle was initially predeflated to osmolarity ratio r = 1.4. The tension threshold 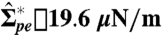 necessary to initiate tube retraction is indicated by an arrow. The fluorescence images show side views of the vesicle (A) before and (B–D) after applying a suction pressure. The images correspond to the points indicated in the graph. The arrowheads in A point to tubes accumulated at the pd interface and extending into the PEG-rich phase. In B–D, the micropipette tip is visible as well as the aspirated vesicle part indicated by arrowheads. At high tensions, no tubes are detected at the two-phase interface (D).
necessary to initiate tube retraction is indicated by an arrow. The fluorescence images show side views of the vesicle (A) before and (B–D) after applying a suction pressure. The images correspond to the points indicated in the graph. The arrowheads in A point to tubes accumulated at the pd interface and extending into the PEG-rich phase. In B–D, the micropipette tip is visible as well as the aspirated vesicle part indicated by arrowheads. At high tensions, no tubes are detected at the two-phase interface (D).

